|
|

¢¹ Sejun An, Dabin Kim, Junggil Kim and Sang Kyu Kim |
|
|
|
"Excited-state chemistry of the nitromethane anion mediated by the dipole-bound states revealed by the photofragment action spectroscopy "
Just accepted. 2023, XXXX
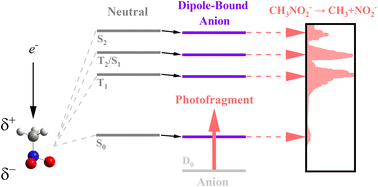
We report the first experimental observation of the excited dipole-bound states (DBS) of the cryogenically-cooled nitromethane anion (CH3NO2-), where the excess electron is loosely attached to the singlet or triplet neutral-core. Photofragment and photodetachment action spectra have been employed for the dynamic exploration of Feshbach resonances located even far above the electron detachment threshold, giving the excitation profiles from the ground anionic state (D0) to the DBSs which match quite well with the spectral structures of the photoelectron spectra. This indicates that the electron transfer from the nonvalence orbital (of DBS) to the valence orbital (of anion) is mainly responsible for the anionic fragmentation channels, giving the strong evidence for that the DBS plays the dynamic doorway-role in the anionic fragmentation reactions. Photofragment action spectra have also been obtained for the anionic clusters of (CH3NO2)2-, (CH3NO2)3-, or (CH3NO2¡¤H2O)-, giving the relative yields of various fragments as a function of the excitation energy for each cluster. The absorption profiles of the anionic clusters exhibit substantial blue-shifts compared to the bare nitromethane anion as its ground state is much stabilized by solvation. The anionic fragmentation pattern varies among different clusters, giving essential clues for the thorough understanding of the whole anionic dynamics such as the dynamic role of the short-lived nonvalence-bound states of the clusters. |
|
[PDF] |
¢¹ Junggil Kim, Kyung Chul Woo, Minseok Kang and Sang Kyu Kim |
|
|
|
"Dynamic Role of the Intramolecular Hydrogen Bonding in the S1 State Relaxation Dynamics Revealed by the Direct Measurement of the Mode-Dependent Internal Conversion Rate of 2-Chlorophenol and 2-Chlorothiophenol "
J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2023, 14,38,8428?8436
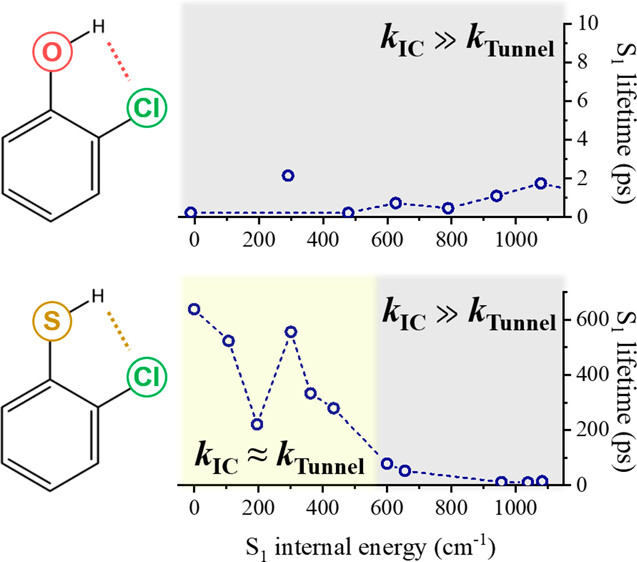
The dynamic role of the intramolecular hydrogen bond in the S1 relaxation of cis-2-chlorophenol (2-CP) or cis-2-chlorothiophenol (2-CTP) has been investigated in a state-specific manner. Whereas ultrafast internal conversion is dominant for 2-CP, the H-tunneling competes with internal conversion for 2-CTP even at the S1 origin. The S0?S1 internal conversion rate of 2-CTP could be directly measured from the S1 lifetimes of 2-CTP-d1 (Cl-C6H4-SD) as the D-tunneling is kinetically blocked, allowing distinct estimations of tunneling and internal conversion rates with increasing the energy. The internal conversion rate of 2-CTP increases by two times at the out-of-plane torsional mode excitation, suggesting that the internal conversion is facilitated at the nonplanar geometry. It then sharply increases at ¡600 cm?1, indicating that the S1/S0 conical intersection is readily accessible at the extended C?Cl bond length. The strength of the intramolecular hydrogen bond should be responsible for the distinct dynamic behaviors of 2-CP and 2-CTP. |
|
[PDF] |
¢¹ Junggil Kim, Kyung Chul Woo and Sang Kyu Kim |
|
|
|
"Mode-dependent H atom tunneling dynamics of the S1 phenol is resolved by the simple topographic view of the potential energy surfaces along the conical intersection seam "
J. Chem. Phys. 2023, 158, 104301
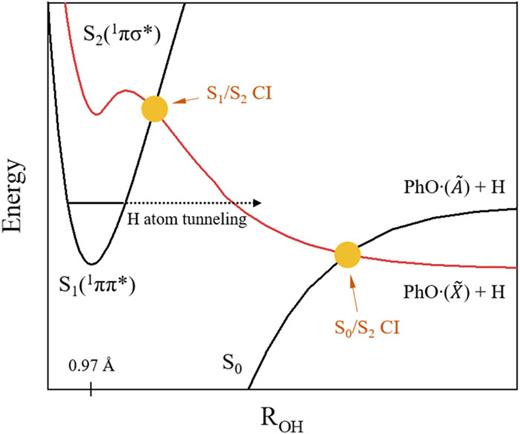
Mode-dependent H atom tunneling dynamics of the O?H bond predissociation of the S1 phenol has been theoretically analyzed. As the tunneling is governed by the complicated multi-dimensional potential energy surfaces that are dynamically shaped by the upper-lying S1(¥ð¥ð*)/S2(¥ð¥ò*) conical intersection, the mode-specific tunneling dynamics of phenol (S1) has been quite formidable to be understood. Herein, we have examined the topography of the potential energy surface along the particular S1 vibrational mode of interest at the nuclear configurations of the S1 minimum and S1/S2 conical intersection. The effective adiabatic tunneling barrier experienced by the reactive flux at the particular S1 vibrational mode excitation is then uniquely determined by the topographic shape of the potential energy surface extended along the conical intersection seam coordinate associated with the particular vibrational mode. The resultant multi-dimensional coupling of the specific vibrational mode to the tunneling coordinate is then reflected in the mode-dependent tunneling rate as well as nonadiabatic transition probability. Remarkably, the mode-specific experimental result of the S1 phenol tunneling reaction [K. C. Woo and S. K. Kim, J. Phys. Chem. A 123, 1529?1537 (2019)] (in terms of the qualitative and relative mode-dependent dynamic behavior) could be well rationalized by semi-classical calculations based on the mode-specific topography of the effective tunneling barrier, providing the clear conceptual insight that the skewed potential energy surfaces along the conical intersection seam (strongly or weakly coupled to the tunneling reaction coordinate) may dictate the tunneling dynamics in the proximity of the conical intersection. |
|
[PDF] |
|
|
|
|

|
¢¹ Junggil Kim, Kyung Chul Woo, Kuk Ki Kim and Sang Kyu Kim |
|
|
|
"¥ð¥ò*-Mediated Nonadiabatic Tunneling Dynamics of Thiophenols in S1: The Semiclassical Approaches "
J. Phys. Chem. A 2022, 126,51,9594-9604

The S-H bond tunneling predissociation dynamics of thiophenol and its ortho-substituted derivatives (2-fluorothiophenol, 2-methoxythiophenol, and 2-chlorothiphenol) in S1 (¥ð¥ð*) where the H atom tunneling is mediated by the nearby S2 (¥ð¥ò*) state (which is repulsive along the S?H bond extension coordinate) have been investigated in a state-specific way using the picosecond time-resolved pump?probe spectroscopy for the jet-cooled molecules. The effects of the specific vibrational mode excitations and the SH/SD substitutions on the S-H(D) bond rupture tunneling dynamics have been interrogated, giving deep insights into the multidimensional aspects of the S1/S2 conical intersection, which also shapes the underlying adiabatic tunneling potential energy surfaces (PESs). The semiclassical tunneling rate calculations based on the Wentzel-Kramers-Brillouin (WKB) approximation or Zhu-Nakamura (ZN) theory have been carried out based on the ab initio PESs calculated in the (one, two, or three) reduced dimensions to be compared with the experiment. Though the quantitative experimental results could not be reproduced satisfactorily by the present calculations, the qualitative trends among different molecules in terms of the behavior of the tunneling rate versus the (adiabatic) barrier height or the number of PES dimensions could be rationalized. Most interestingly, the H/D kinetic isotope effect observed in the tunneling rate could be much better explained by the ZN theory compared to the WKB approximation, indicating that the nonadiabatic coupling matrix elements should be invoked for understanding the tunneling dynamics taking place in the proximity of the conical intersection. |
|
[PDF] |
¢¹ Do Hyung Kang, Jinwoo Kim Han Jun Eun and Sang Kyu Kim |
|
|
|
"State-Specific Chemical Dynamics of the Nonvalence Bound State of the Molecular Anions "
Acc. Chem. Res. 2022, 55,20,3032-3042
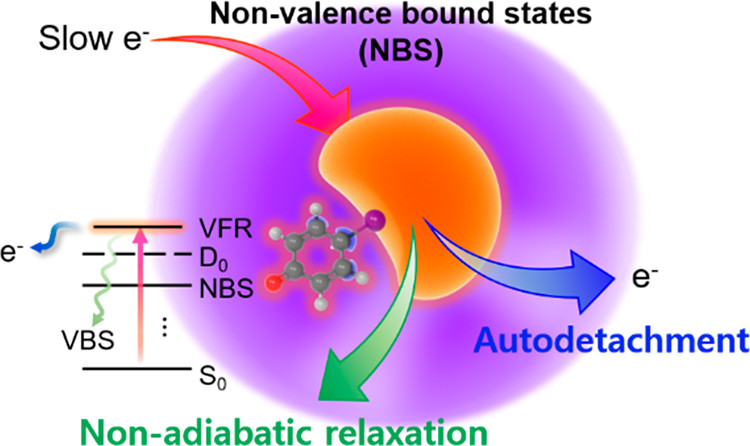
Nonvalence bound states (NBS) are anionic states where the excess electron is extremely loosely bound to the neutral core through long-range potentials. In contrast to the valence orbitals of which the electron occupancy determines the molecular structure, as well as the chemical reactivity, the nonvalence orbital is quite diffuse and located far from the neutral core. The NBS can be classified into the dipole-bound state (DBS), quadruple-bound state (QBS), or correlation-bound state (CBS) according to the nature of the electron-neutral interaction, although their interaction potentials may cooperatively contribute. The NBS is ubiquitous in nature and has the strong implications in atmospheric, interstellar, or biological chemistry. Accordingly, NBS has long been conceived to play the role of the doorway into the formation of a stable anion or dissociative electron attachment (DEA). Despite intensive and extensive studies, however, the quantum-mechanical nature of NBS is still far from being thorough understanding. Herein, we describe a new aspect of state-specific NBS-mediated chemical dynamics, which has been revealed through a series of recent studies by our group. We have employed picosecond time-resolved pump-probe spectroscopy combined with cryogenically cooled ion trap and velocity-map imaging techniques to study closed-shell anions generated by electrospray ionization. DBS vibrational Feshbach resonances are prepared by the optical excitation of phenoxide, for instance, and their individual lifetimes have been precisely measured in a state-specific manner to reveal the strong mode-dependency of the autodetachment rate. Fermi¡¯s golden rule turns out to be extremely useful for a rational explanation of the experiment, although the more sophisticated theoretical model is desirable for the more quantitative analysis. For the DBS of para-chlorophenoxide or para-bromophenoxide where the polarizability of neutral core is substantial, the Fermi¡¯s golden rule based on the charge-dipole potential needs to be significantly modified to include the correlation effects to explain the exceptionally slow autodetachment rates. For the QBS of 4-cyanophenoxide, the mode-specific behavior of the quadrupole ellipsoid tensor explains the strong mode-dependent autodetachment rate. Meanwhile, the nonadiabatic transition of the excess electron into the valence orbital can result in stable anion formation or immediate chemical bond rupture. In the DBS of ortho-, meta-, or para-iodophenoxide, the transformation of the loosely bound excess electron into the ¥ð¥ò* antibonding orbital occurs to give I- as a final fragment. The fragmentation mediated by DBS occurs competitively with the concomitant autodetachment, paving a new way of the reaction control by tuning the quantum-mechanical nature of the DBS Feshbach resonance. This experimental observation provides the foremost evidence for the dynamic role of the DBS as a doorway into anion chemistry, such as DEA. The ponderomotive force on the electron in the nonvalence orbital has been demonstrated for the first time in a strong optical field, giving great promise for the manipulation of polyatomic molecules in terms of the spatial location, as well as the AC-Stark control of the chemical reaction. |
|
[PDF] |
¢¹ Do Hyung Kang, Jinwoo Kim Han Jun Eun and Sang Kyu Kim |
|
|
|
"Experimental Observation of the Resonant Doorways to Anion Chemistry: Dynamic Role of Dipole-Bound Feshbach Resonances in Dissociative Electron Attachment "
J.Am. Chem. Soc. 2022, 144,35, 16077-16085
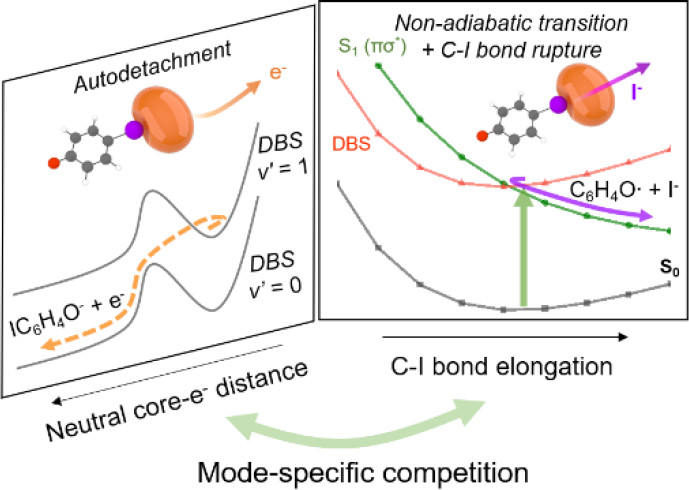
Anion chemical dynamics of autodetachment and fragmentation mediated by the dipole-bound state (DBS) have been thoroughly investigated in a state-specific way for the first time by employing the picosecond time-resolved or the nanosecond frequency-resolved spectroscopy combined with the cryogenically cooled ion trap and velocity-map imaging techniques. For the ortho-, meta-, or para-iodophenoxide anion (o-, m-, or p-IPhO-), the C-I bond rupture giving the anionic iodide (I-) fragment occurs via the nonadiabatic transition from the DBS to the nearby valence-bound states (VBS) of the anion where the vibronic coupling into the S1 (¥ð-sigma*) state (which is repulsive along the C-I bond extension coordinate) should be largely responsible. The dynamic details are governed by the isomer-specific nature of the potential energy surfaces in the vicinity of the DBS-VBS curve crossings, as manifested in the huge different chemical reactivity of o-, m-, or p-IPhO-. It is confirmed here that the C-I bond dissociation is mediated by DBS resonances, providing the foremost evidence that the metastable DBS plays the essential role as the doorway into the anion chemistry especially of the dissociative electron attachment (DEA). The fragmentation channel is dominant when it is mediated by the DBS resonances located below the electron-affinity (EA) threshold, whereas it is kinetically adjusted by the competitive autodetachment process when the DBS resonances lying above EA convey the electron to the valence orbitals. The product yield of the C-I bond cleavage is strongly mode-dependent as the rate of the concomitant autodetachment is much influenced by the characteristics of the individual vibrational modes, paving a new way of the reaction control of the anion chemistry. |
|
[PDF] |
¢¹ Michael N. R. Ashfold and Sang Kyu Kim |
|
|
|
"Non-Born-Oppenheimer effects in molecular photochemistry: an experimental perspective "
Phil. Trans. R. Soc. A 2022, 380 20200376
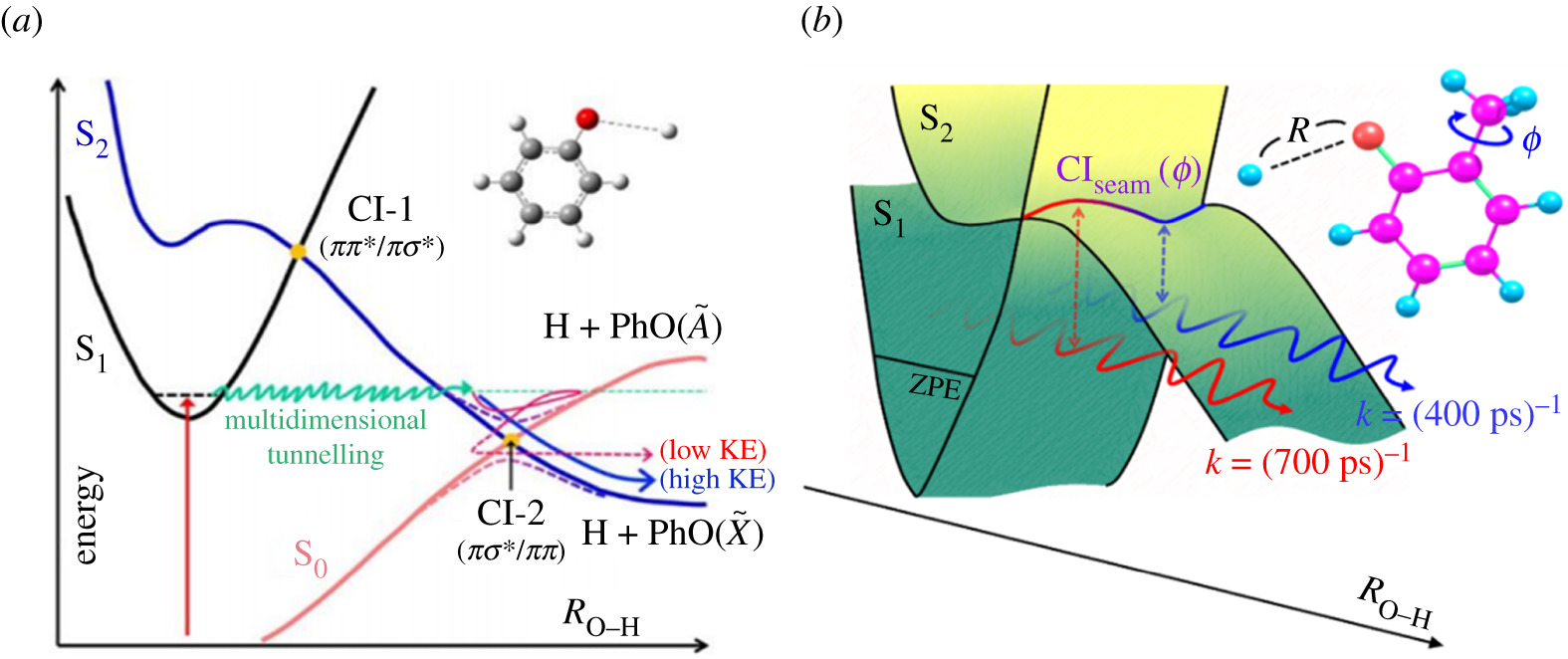
Non-adiabatic couplings between Born-Oppenheimer (BO)-derived potential energy surfaces are now recognized as pivotal in describing the non-radiative decay of electronically excited molecules following photon absorption. This opinion piece illustrates how non-BO effects provide photostability to many biomolecules when exposed to ultraviolet radiation, yet in many other cases are key to facilitating ¡®reactive¡¯ outcomes like isomerization and bond fission. The examples are presented in order of decreasing molecular complexity, spanning studies of organic sunscreen molecules in solution, through two families of heteroatom containing aromatic molecules and culminating with studies of isolated gas phase H2O molecules that afford some of the most detailed insights yet available into the cascade of non-adiabatic couplings that enable the evolution from photoexcited molecule to eventual products. |
|
[PDF] |
|
¢¹ Do Hyung Kang, Jinwoo Kim and Sang Kyu Kim |
|
|
|
"Dynamic role of the correlation effect revealed in the exceptionally slow autodetachment rates of the vibrational Feshbach resonances in the dipole-bound state "
Chem.Sci, 2022, 13.2714
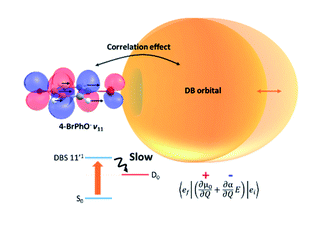
Real-time autodetachment dynamics of the loosely bound excess electron from the vibrational Feshbach resonances of the dipole-bound states (DBS) of 4-bromophonoxide (4-BrPhO-) and 4-chlorophenoxide (4-ClPhO-) anions have been thoroughly investigated. The state-specific autodetachment rate measurements obtained by the picosecond time-resolved pump-probe method on the cryogenically cooled anions exhibit an exceptionally long lifetime (¥ó) of ¡823 ¡¾ 156 ps for the 11¡Ç1 vibrational mode of the 4-BrPhO- DBS. Strong mode-dependency in the wide dynamic range has also been found, giving ¥ó ¡ 5.3 ps for the 10¡Ç1 mode, for instance. Though it is nontrivial to get the state-specific rates for the 4-ClPhO- DBS, the average autodetachment lifetime of the 19¡Ç120¡Ç1/11¡Ç1 mode has been estimated to be ¡548 ¡¾ 108 ps. Observation of these exceptionally slow autodetachment rates of vibrational Feshbach resonances strongly indicates that the correlation effect may play a significant role in the DBS photodetachment dynamics. Fermi's golden rule has been invoked so that the correlation effect is taken into account in the form of the interaction between the charge and the induced dipole where the latter is given by the polarizable counterparts of the electron-rich halogenated compound and the diffuse non-valence electron. This report suggests that one may measure, from the real-time autodetachment dynamics, the extent of the correlation effect contribution to the stabilization and/or dynamics of the excess non-valence electron among many different types of long-range interactions of the DBS. |
|
[PDF] |
|
|


|
¢¹ Junggil Kim,Kyung Chul Woo,Kuk Ki Kim,Minseok Kang,Sang Kyu Kim |
|
|
|
"Tunneling dynamics dictated by the multidimensional conical intersection seam in the ¥ð¥ò*-mediated photochemistry of heteroaromatic molecules "
Bull.Korean Chem.Soc, 2021, Volume43 Issue2.
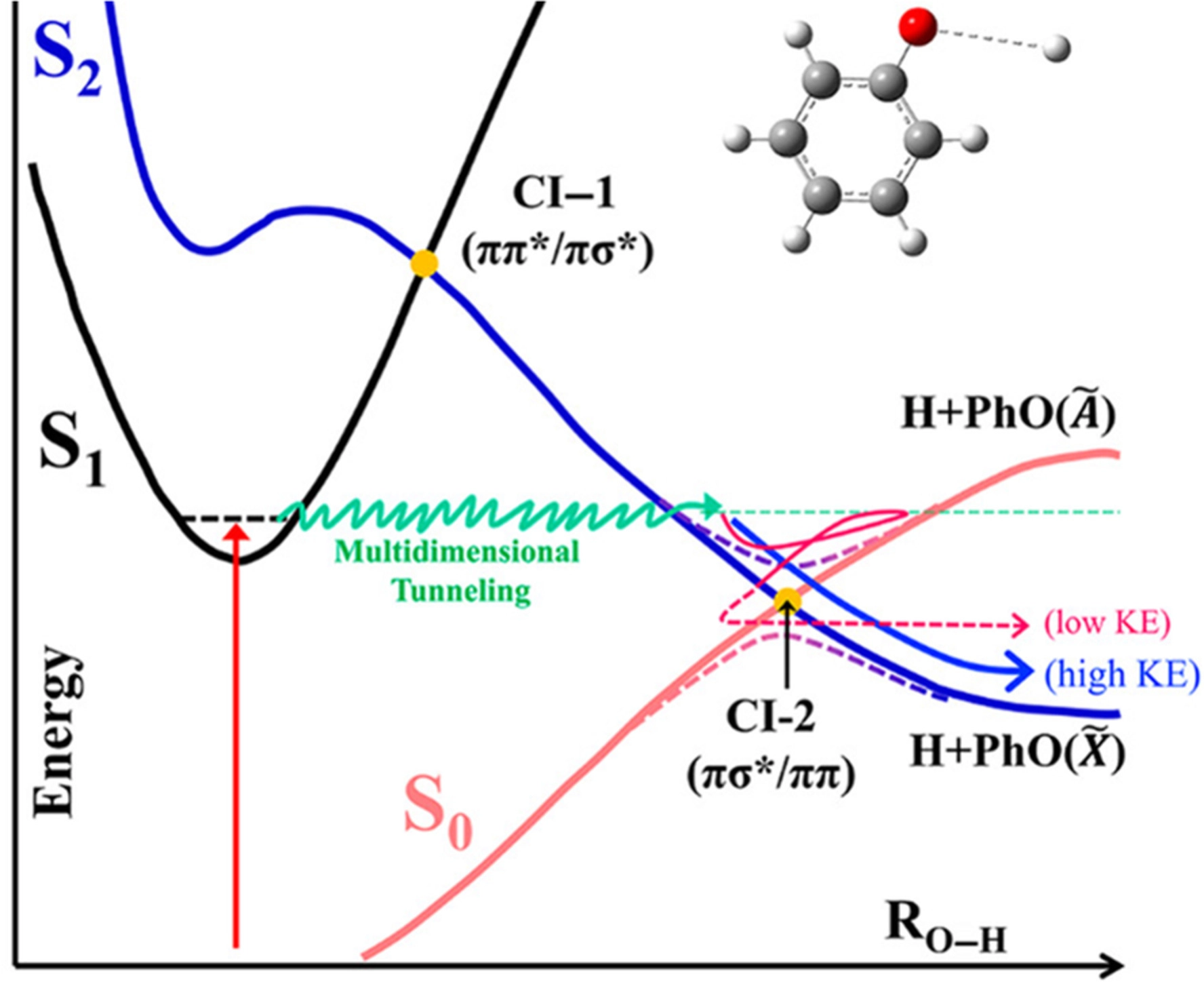
The ¥ð¥ò*-mediated photochemistry of heteroaromatic molecules has provoked the investigation of the conical intersection dynamics. The Born-Oppenheimerapproximation fails at the conical intersection where the S1(¥ð¥ð*) and S2(¥ð¥ò*)states cross. The nonadiabatic transitions are much influenced by the nuclear con-figuration of the reactive flux particularly in the curve-crossing region encountered along the reaction pathway. In this article, we focus on the tunnelingdynamics of phenols and thiophenols. The O (S)-H bond cleavage occurs viatunneling through the barrier which is dynamically shaped by the upper-lying S1/S2 conical intersection in terms of the couplings at the individual branchingplanes as well as along the (3N-8) dimensional seam coordinates. State-specific tunneling rates and their interpretation are given for phenol, substituted phenols,thiophenol,ortho-substituted thiophenols, and benzenediols including their 1:1water clusters. The completely orthogonal modes to the tunneling coordinate arevery critical in the dynamic shaping of the reaction barrier. |
|
[PDF] |
|
¢¹ Do Hyung Kang, Jinwoo Kim and Heung-Ryoul Noh & Sang Kyu Kim |
|
|
|
"Observation of the ponderomotive effect in non-valence bound states of polyatomic molecular anions "
Nat Commun 12, 7098, (2021)
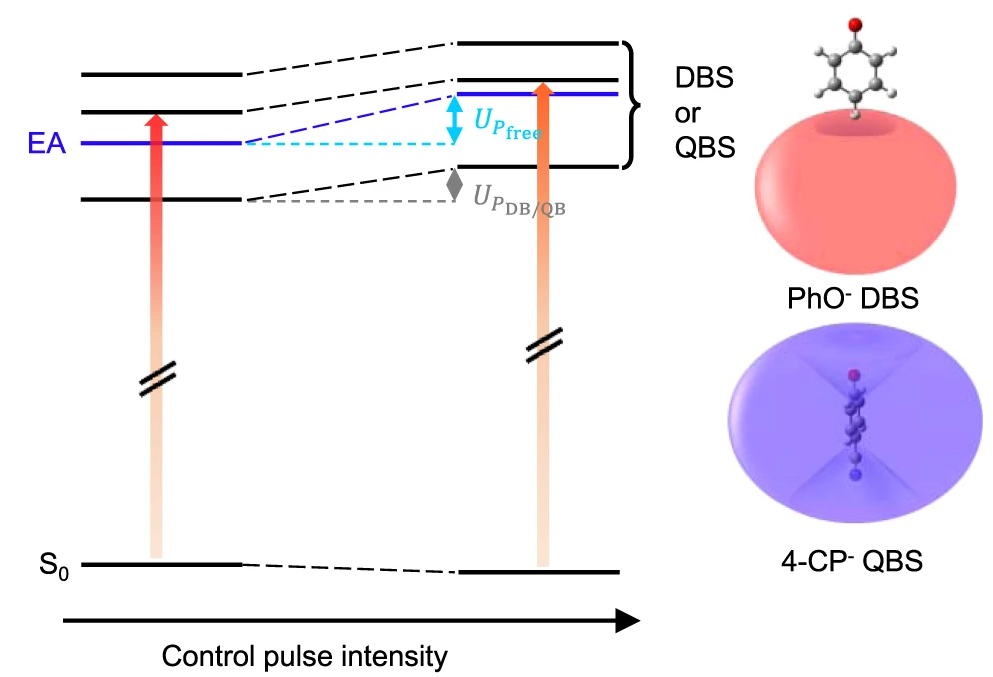
The ponderomotive force on molecular systems has rarely been observed hitherto, despite potentially being extremely useful for the manipulation of the molecular properties. Here, the ponderomotive effect in the non-valence bound states has been experimentally demonstrated, for the first time to the best of our knowledge, giving great promise for the manipulation of polyatomic molecules by the dynamic Stark effect. Entire quantum levels of the dipole-bound state (DBS) and quadrupole-bound state (QBS) of the phenoxide (or 4-bromophenoxide) and 4-cyanophenoxide anions, respectively, show clear-cut ponderomotive blue-shifts in the presence of the spatiotemporally overlapped non-resonant picosecond control laser pulse. The quasi-free electron in the QBS is found to be more vulnerable to the external oscillating electromagnetic field compared to that in the DBS, suggesting that the non-valence orbital of the former is more diffusive and thus more polarizable compared to that of the latter. |
|
[PDF] |
|
¢¹ Kuk Ki Kim, Junggil Kim, Kyung Chul Woo, and Sang Kyu Kim |
|
|
|
"S1-State Decay Dynamics of Benzenediols (Catechol, Resorcinol, and Hydroquinone) and Their 1:1 Water Clusters "
J. Phys. Chem.A., 2021, 125, 35, 7655-7661
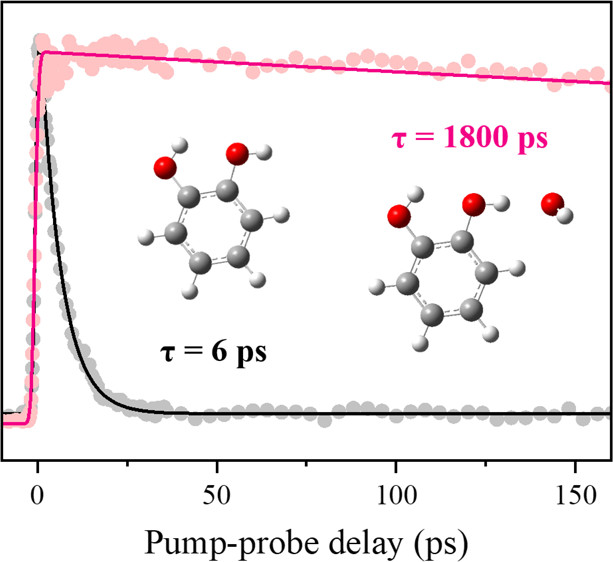
The S1-state decaying rates of the three different benzenediols, catechol, resorcinol, and hydroquinone, and their 1:1 water clusters have been state-specifically measured using the picosecond time-resolved parent ion transients obtained by the pump (excitation) and probe (ionization) scheme. The S1 lifetime of catechol is found to be short, giving ¥ó ¡ 5.9 ps at the zero-point level. This is ascribed to the H-atom detachment from the free OH moiety of the molecule. Consistent with a previous report (J. Phys. Chem. Lett.2013, 4, 3819-3823), the S1 lifetime gets lengthened with low-frequency vibrational mode excitations, giving ¥ó ¡ 9.0 ps for the 116 cm-1 band. The S1 lifetimes at the additional vibronic modes of catechol are newly measured, showing the nonnegligible mode-dependent fluctuations of the tunneling rate. When catechol is complexed with water, the S1 lifetime is enormously increased to ¥ó ¡ 1.80 ns at the zero-point level while it shows an unusual dip at the intermolecular stretching mode excitation (¥ó ¡ 1.03 ns at 146 cm-1). Otherwise, it is shortened monotonically with increasing the internal energy, giving ¥ó ¡ 0.67 ns for the 856 cm-1 band. Two different asymmetric or symmetric conformers of resorcinol give the respective S1 lifetimes of 4.5 or 6.3 ns at their zero-point levels according to the estimation from our transients taken within the temporal window of 0?2.7 ns. When resorcinol is 1:1 complexed with H2O, the S1 decaying rate is slightly accelerated for both conformers. The S1 lifetimes of trans and cis forms of hydroquinone are measured to be more or less same, giving ¥ó ¡ 2.8 ns at the zero-point level. When H2O is complexed with hydroquinone, the S1 decaying process is facilitated for both conformers, slightly more efficiently for the cis conformer. |
|
[PDF] |
|
¢¹ Junggil Kim and Sang Kyu Kim |
|
|
|
"Multiphoton-excited dynamics of the trans or cis structural isomer of 1,2-dibromoethylene "
J. Chem.Phys., 155, 164304, (2021)
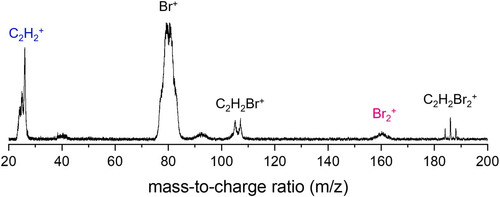
Photofragmentation dynamics of cis and trans isomers of 1,2-dibromoethylene (1,2-DBE) have been investigated by multiphoton excitation using a picosecond (ps) laser pulse. It has been found that the Br2+ product ion preferentially originates from the cis isomer rather than from trans. The Boltzmann-type isotropic low kinetic energy components of the Br+ and Br2+product state distributions seem to be most likely from the unimolecular reactions of the vibrationally hot cationic ground state generated by the three-photon absorption at the photon energy below ~ 38000 cm-1. The highly anisotropic kinetic energy components of Br+ and Br2+ start to appear at the photon energy above ~38000 cm-1, where the Dn (n ≥1) - D0 transition is facilitated within the same ps laser pulse as the parent molecule is efficiently ionized by the two-photon absorption. The transition dipole moment of the D4 - D0 transition of the strongest oscillator strength has been theoretically predicted to be parallel to the C-Br bond or C=C bond axis for the trans or cis isomer, respectively. The fast anisotropic with the (ß ~ +2) component in the Br+ product distribution is thus likely from the trans isomer, whereas that of Br2+ (ß~-0.5) should be the consequence of the photodissociation of the cis isomer. The isomer-specific reactivity found here in the picosecond multiphoton excitation of 1,2-DBE provides a nice platform for the better understanding of the structure?reactivity relationship under the harsh condition of the strong or ultrashort optical field. |
|
[PDF] |
|
¢¹ Junggil Kim, Kyung Chul Woo and Sang Kyu Kim |
|
|
|
"Femtosecond Wavepacket Dynamics Reveals the Molecular Structures in the Excited (S1) and Cationic (D0) States"
J. Phys. Chem. A., 2021, 125, 30, 6629-6635
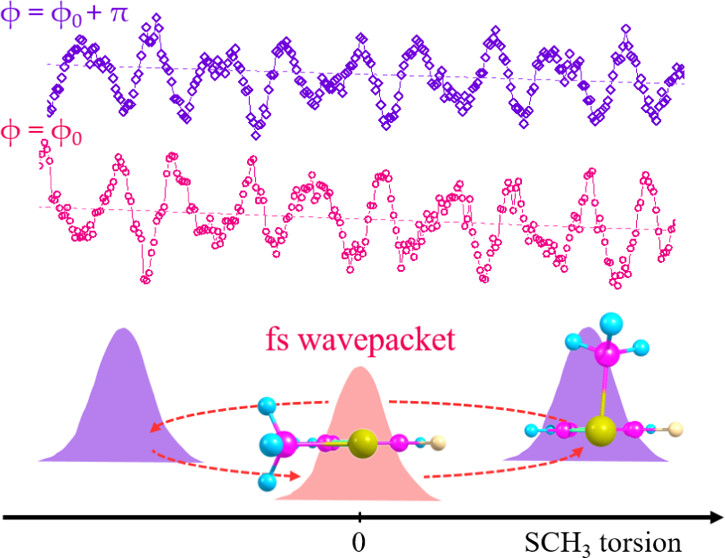
Molecular structures in the electronically excited (S1) and cationic (D0) states of 2-fluorothioanisole (2-FTA) have been precisely refined from the real-time dynamics of the femtosecond (fs) wavepacket prepared by the coherent excitation of the Franck-Condon active out-of-plane torsional modes in the S1 ¡ç S0 transition at 285 nm. The simulation to reproduce the experiment in terms of the beating frequencies gives the nonplanar geometry of 2-FTA in S1, where the out-of-plane dihedral angle (¥õ) of the S-CH3 moiety is 51¡Æ with respect to the molecular plane. The behavior of the fs wavepacket in terms of the amplitudes and phases with the change of the probe (ionization) wavelength (¥ëprobe= 300?330 nm) provides the otherwise veiled structure of the cationic D0 state. While the 2-FTA cation adopts the planar geometry (¥õ = 0¡Æ) at the global minimum, it is found to have a vertical minimum at ¥õ ≈ 135¡Æ from the perspective of the D0 ¡ç S1 vertical transition. Ab initio calculations support the experiment quite well although the simulation using the model potentials could improve the match with the experiment, giving the new interpretation for the previously disputed photoelectron spectroscopic results. |
|
[PDF] |
|
¢¹ Do Hyung Kang, Jinwoo Kim and Sang Kyu Kim |
|
|
|
"Recapture of the Nonvalence Excess Electron into the Excited Valence Orbital Leads to the Chemical Bond Cleavage in the Anion"
J. Phys. Chem. Lett., 2021, 12, 27, 6383-6388
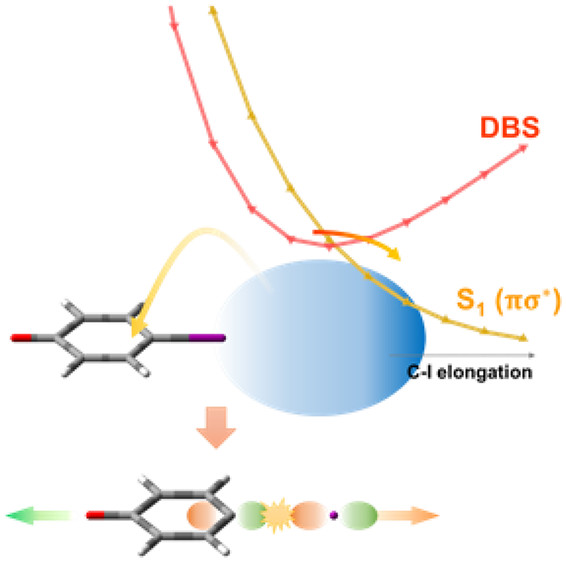
The excess electron in the dipole-bound state (DBS) of the anion is found to be recaptured into the excited valence orbital localized at the positive end of the dipole, leading to the chemical bond cleavage of the anion. In the DBS of the 4-iodophenoxide anion, the extremely loosely bound electron (binding energy of 53 cm-1) is recaptured into the ¥ð¥ò* valence orbital, which is repulsive along the C-I bond extension coordinate, leading to the iodide (I-) and phenoxyl diradical (¡¤C6H4O¡¤) channel at the asymptotic limit. This is the first real-time observation of the state-specific relaxation (other than autodetachment) dynamics of the DBS and subsequent chemical reaction. The lifetime of the 4-iodophenoxide DBS at its zero-point energy (ZPE), which is measured for the cryogenically cooled trapped anion using the picosecond laser pump-probe scheme, has been estimated to be ¡9.5 ¡¾ 0.3 ps. Quantum mechanical calculations support the efficient transition from the DBS (below the detachment threshold) to the low-lying ¥ð¥ò* valence orbital of the first excited state of the anion. Similar experiments on 4-chlorophenoxide and 4-bromophenoxide anions indicate that the electron recaptures into excited valence orbitals hardly occur in the DBS of those anions, giving the long lifetimes (¡íns) at ZPE, suggesting that the internal conversion to S0 may be the major relaxation pathway for those anions. |
|
[PDF] |
|
¢¹ Do Hyung Kang, Jinwoo Kim, Min Cheng and Sang Kyu Kim |
|
|
|
"Mode-Specific Autodetachment Dynamics of an Excited Non-valence Quadrupole-Bound State"
J. Phys. Chem. Lett., 2021, 12, 7, 1947-1954
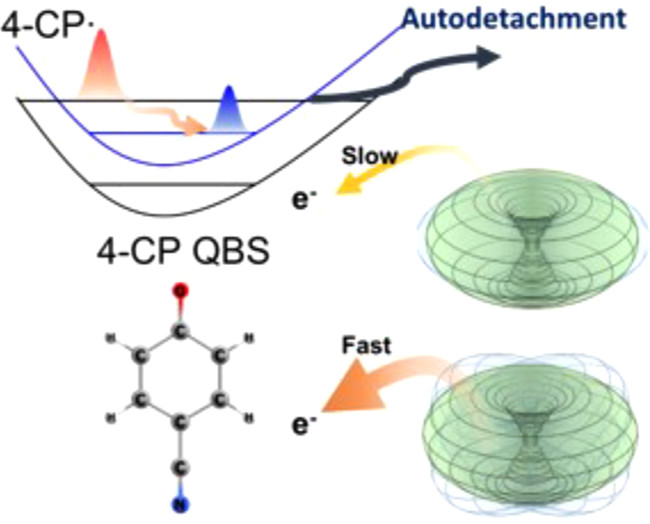
The autodetachment dynamics of vibrational Feshbach resonances of the quadrupole-bound state (QBS) for the first time has been investigated in real time for the first excited state of the 4-cyanophenoxide (4-CP) anion. Individual vibrational resonances of the cryogenically cooled 4-CP QBS have been unambiguously identified, and their autodetachment rates state-specifically measured using the picosecond time-resolved pump-probe technique employing the photoelectron velocity-map imaging method. The autodetachment lifetime (τ) is found to be strongly dependent on mode, giving τ values of ~56, ~27, and ≤ 2.8 ps for the 12¡Ç1 (Evib = 406 cm-1), 12¡Ç2 (Evib = 806 cm-1), and 21¡Ç1 (Evib = 220 cm-1) modes, respectively. The striking mode-specific behavior of the QBS lifetime has been invoked by the physical model in which the loosely bound electron falls off by the dynamic wobbling of the three-dimensional quadrupole moment ellipsoid associated with the corresponding vibrational motion in the autodetachment process. |
|
[PDF] |
¢¹ Kyung Chul Woo, Junggil Kim and Sang Kyu Kim |
|
|
|
"Conformer-Specific Tunneling Dynamics
Dictated by the Seam Coordinate of the Conical Intersection"
J. Phys. Chem. Lett., 2021, 12, 7, 1854-1861
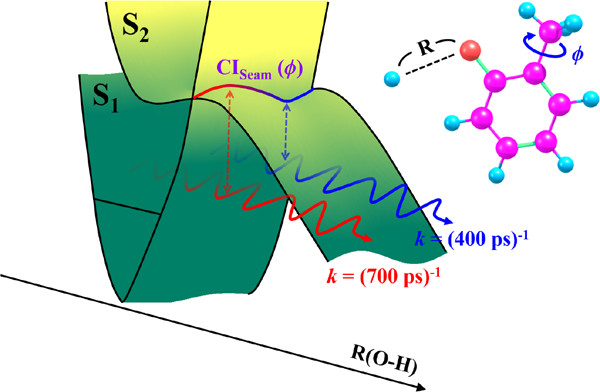
The dynamic role of the conical intersection "seam" coordinate has been first revealed in the H fragmentation reaction of ortho(o)-cresol conformers. One of the (3N - 8) dimensional seam coordinates of the S1(ππ*)/S2(πσ*) conical intersection has been identified as the CH3 torsional potential function. The tunneling dynamics of the reactive flux is dictated by its nuclear layout with respect to the CH3 torsional angle, as the multidimensional tunneling barrier is dynamically shaped along the conical intersection seam. The effective tunneling-barrier weight-averaged over the quantum-mechanical probability along the CH3 torsional angle perfectly explains the experimental finding: the sharp variation of the tunneling rate ((700-400) ps-1) with the CH3 torsional mode excitations within the narrow (0-100 cm-1) energetic window. The much longer S1 lifetime of cis compared to trans is ascribed to the higher-lying S1/S2 conical intersection of the former. With the use of distinct lifetimes, vibronic bands of each conformer could be completely separated. |
|
[PDF] |
¢¹ Dong-gu Kang, Kyung Chul Woo, Do Hyung Kang, Chanho Park and Sang Kyu Kim |
|
|
|
"Improved Spectral Resolution of the Femtosecond Stimulated Raman Spectroscopy
Achieved by the use of the 2nd-order Diffraction Method"
Sci. Rep., 11, 3361, (2021)
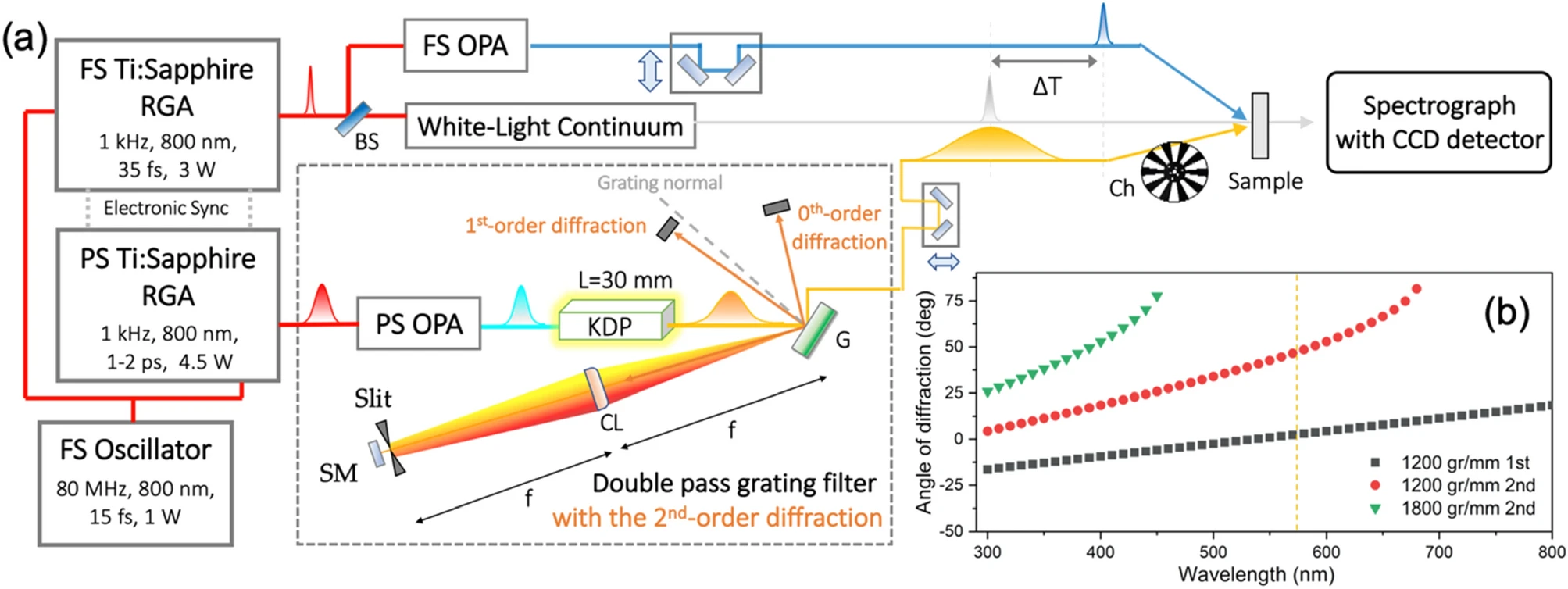
Prolongation of the picosecond Raman pump laser pulse in the femtosecond stimulated Raman spectroscopy (FSRS) setup is essential for achieving the high spectral resolution of the time-resolved vibrational Raman spectra. In this work, the 2nd-order diffraction has been firstly employed in the double-pass grating filter technique for realizing the FSRS setup with the sub-5 cm-1 spectral resolution. It has been experimentally demonstrated that our new FSRS setup gives rise to a highly-resolved Raman spectrum of the excited trans-stilbene, which is much improved from those reported in the literatures. The spectral resolution of the present FSRS system has been estimated to be the lowest value ever reported to date, giving Δν = 2.5 cm-1. |
|
[PDF] |
|
|


|
¢¹ JunWoo Kim, Dong-gu Kang, Sang Kyu Kim and Taiha Joo |
|
|
|
"Role of coherent nuclear motion in the ultrafast intersystem crossing of ruthenium complexes"
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2020, 22, 25811-25818
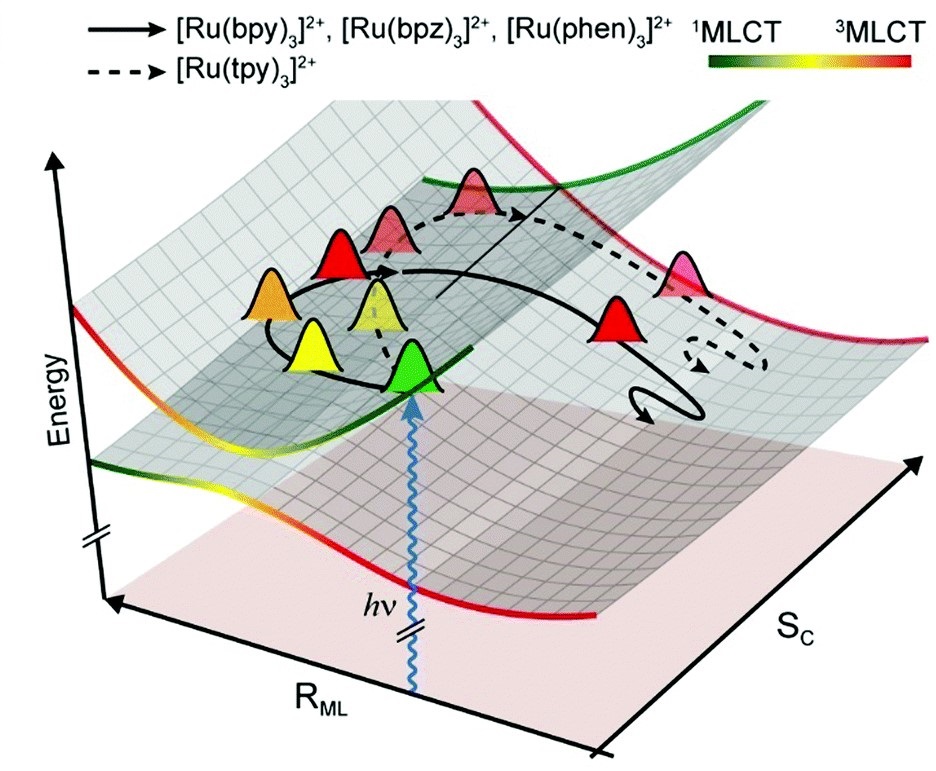
Ultrafast intersystem crossing (ISC) in transition metal complexes leads to a long-lived active state with a high yield, which leads to efficient light energy conversion. The detailed mechanism of ISC may lead to a rational molecular design of superior transition metal complexes. Coherent nuclear wave packets observed in femtosecond time-resolved spectroscopies provide important information on the excited-state dynamics. In particular, analyzing the nuclear wave packets in both the reactant and the product may unveil the molecular dynamics of an ultrafast reaction. In this study, experimental evidence proving the reaction coordinates of the ultrafast ISC of ruthenium(II) complexes is presented using coherent vibrational spectroscopy with a quantum chemical simulation of coherent vibrational motion. We observed vibrational modes strongly coupled to the ISC, whose vibrational coherences undergo remarkable attenuation after the ISC. The coupled modes contain metal-ligand stretching or symmetry breaking components, and the faster ISC rates of lower-symmetry ruthenium(II) complexes support the significance of the latter. |
|
[PDF] |
¢¹ Do Hyung Kang, Sejun An and Sang Kyu Kim |
|
|
|
"Real-time Autodetachment Dynamics of Vibrational Feshbach Resonances in a Dipole-bound State"
Phys. Rev. Lett., 125, 093001
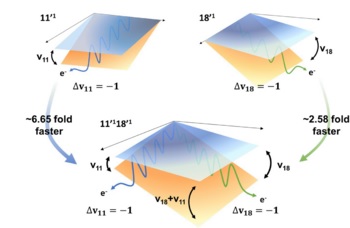
Feshbach resonances corresponding to metastable vibrational states of the dipole-bound state (DBS) have been interrogated in real time for the first time. The state-specific autodetachment rates of the DBS of the phenoxide anion in the cryogenically cooled ion trap have been directly measured, giving τ ¡ 33.5 ps for the lifetime of the most prominent 11'1 mode (519 cm-1). Overall, the lifetime of the individual DBS state is strongly mode dependent to give τ ¡ 5 ps for the 18'1 mode (632 cm-1) and τ ¡ 12 ps for the 11'2 mode (1036 cm-1). The qualitative trend of the experiment could be successfully explained by the Fermi¡¯s golden rule. Autodetachment of the 11'118'1 combination mode is found to be much accelerated (τ ¡Â 1.4 ps) than expected, and its bifurcation dynamics into either the 111180 or 110181 state of the neutral core radical, according to the propensity rule of Δv = -1, could be distinctly differentiated through the photoelectron images to provide the unprecedented deep insights into the interaction between electronic and nuclear dynamics of the DBS, challenging the most sophisticated theoretical calculations. |
|
[PDF] |
¢¹ Heesung Lee and Sang Kyu Kim |
|
|
|
"Vibration Mediated Photodissociation Dynamics of CH3SH:
Manipulation of the Dynamic Energy Disposal into Products"
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2020, 22, 19713-19717
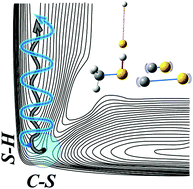
The S-H bond dissociation dynamics of CH3SH have been investigated for the S1-S0 transition mediated by either the S-H stretching (2608 cm-1) or CH3 symmetric stretching (2951 cm-1) mode excitation in the S0 state. The S-H and C-S bond extensions are strongly coupled in the S1 state through the S1/S2 same-symmetry conical intersection, giving the C-S stretching mode excitation of the CH3S• fragment during the prompt S-H bond rupture on S1. In the IR + UV transition mediated by the S-H stretching mode, the vertical transition seems to access the Franck-Condon region where the S-H bond is shortened while the coupling to the C-S bond stretching becomes stronger compared to the case of one-photon UV transition, indicating that the intramolecular vibrational redistribution (IVR) is little activated in S0. When the IR + UV excitation is mediated by the CH3 symmetric stretching mode, on the other hand, the Franck-Condon region in S1 encompasses the enlarged molecular structures with respect to both S-H and C-S bond extensions, presumably due to the rapid IVR in S0 prior to the vertical transition. This leads to the inverted vibrational state population of the C-S bond stretching mode of the CH3S• fragment. This work demonstrates that the reaction dynamics upon the IR + UV excitation of CH3SH is highly mode dependent and the energy disposal dynamics could be controlled by the manipulation of the Franck-Condon region through the particular vibrational-state mediation in the ground state, shedding new light on the structure-dynamics relationship. |
|
[PDF] |
¢¹ Junggil Kim, Jean Sun Lim, Heung-Ryoul Noh and Sang Kyu Kim |
|
|
|
"Experimental Observation of the Autler-Townes Splitting in Polyatomic Molecules"
J. Phys. Chem. Lett., 2020, 11 (16), 6791-6795
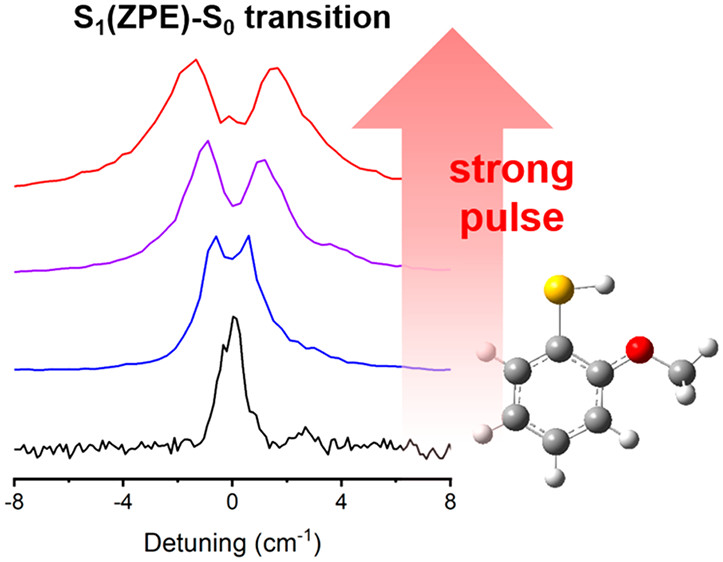
Autler-Townes (AT) splitting has been experimentally observed in the optical transition between the zero-point levels of S1 and S0 for the supersonically cooled 2-methoxythiophenol, 2-fluorothiophenol, and 2-chlorothiophenol. This is the first experimental observation of the light-dressed quantum states of polyatomic molecules (N > 3) in the electronic transition. In the resonance-enhanced ionization process involving the optically-coupled states, if Rabi cycling is ensured within the nanosecond laser pulse, the AT splitting is clearly observed for the open system of which the excited-state lifetime is shorter than hundreds of ps. Semi-classical optical Bloch equations and dressed-atom approach based on the three-level atomic model describe the experiment quite well, giving deep insights into the light-matter interaction in polyatomic molecular systems. |
|
[PDF] |
¢¹ Kyung Chul Woo and Sang Kyu Kim |
|
|
|
"Real-Time Tunneling Dynamics through Adiabatic Potential Energy Surfaces
Shaped by a Conical Intersection"
J. Phys. Chem. Lett., 2020, 11 (16), 6730-6736
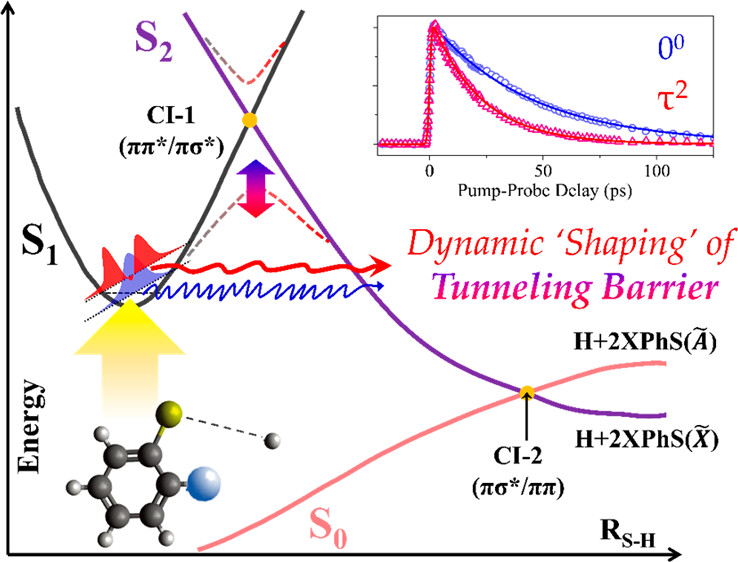
Dynamic shaping of the adiabatic tunneling barrier in the S-H bond extension coordinate of several ortho-substituted thio-phenols has been found to be mediated by low-frequency out-of-plane vibrational modes, which are parallel to the coupling vector of the branching plane comprising the conical intersection. The S-H predissociation tunneling rate (k) measured when exciting to the S1 zero-point level of 2-methoxythiophenol (44 ps)-1 increases abruptly, to k ~ (22 ps)-1, at the energy corre-sponding to excitation of the 152 cm-1 out-of-plane vibrational mode, then falls back to k ~ (40 ps)-1 when exciting the in-plane mode at 282 cm-1. Similar resonance-like peaks in plots of S1 tunneling rate versus internal energy are observed when exciting the corresponding low-frequency out-of-plane modes in the S1 states of 2-fluorothiophenol and 2-chlorothiophenol. This experiment provides clear-cut evidence for dynamical ¡°shaping¡± of the lower-lying adiabatic potential energy surfaces by the higher-lying conical intersection seam, which dictates the multidimensional tunneling dynamics. |
|
[PDF] |
¢¹ Heesung Lee, So-Yeon Kim and Sang Kyu Kim |
|
|
|
"Multidimensional Characterization of the Conical Intersection Seam in the Normal Mode Space"
Chem. Sci., 2020, 11, 6856-6861
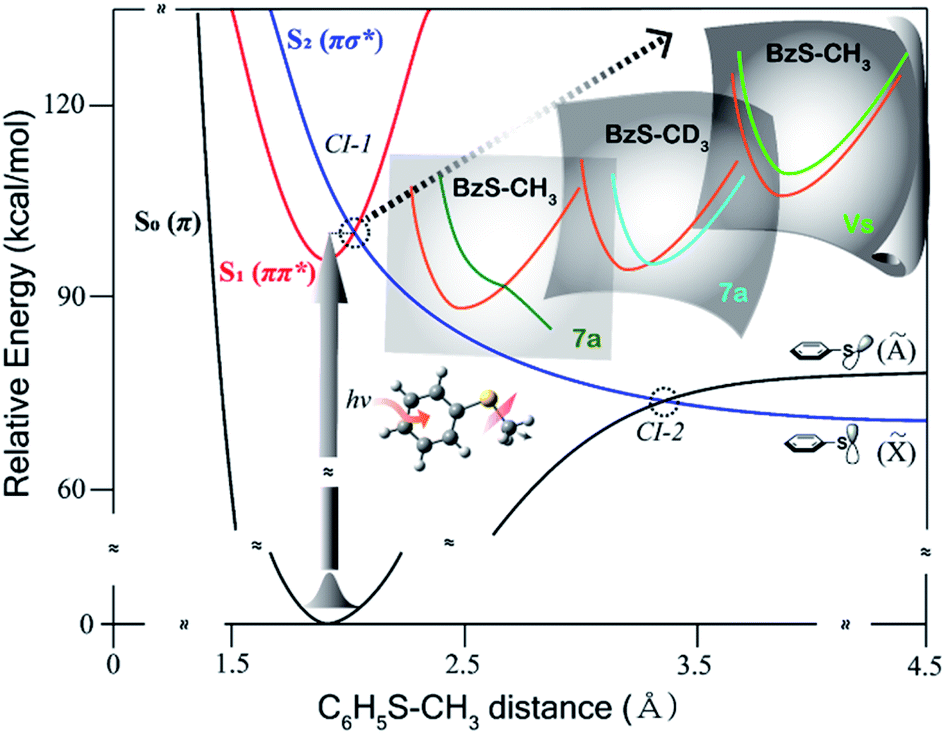
Multidimensional conical intersection seam has been characterized by utilizing the dynamic resonances in the nonadiabatic transition probability experimentally observed in the predissociation of thioanisole isotopomers. The nonadiabatic bifurcation behavior of the reactive flux into either the Herzbergl type-I (electronic) or type-II (vibrational) predissociation pathway is found to be strongly dependent on the quantum nature of the S1/S2 vibronic eigenstate, providing the essential information about structure and dynamic character of the conical intersection seam projected onto the normal mode space. By modifying the nature of the normal mode space through partial or full H/D substitution of the molecule, multiple aspects of the conical intersection seam could be characterized from different viewpoints set by the adjusted normal mode space. Theoretical calculations of potential energy curves along selected normal mode displacements support the experiment. |
|
[PDF] |
¢¹ Heesung Lee, So-Yeon Kim, Jean Sum Lim, Junggil Kim and Sang Kyu Kim |
|
|
"Conformer Specific Excited-State Structure of 3-Methylthioanisole"
J. Phys. Chem. A, 2020, 124 (23), pp 4666-4671

Trans and cis conformers of 3-methylthioanisole have been spectroscopically investigated to reveal the conformer specific structural changes upon the S1 (¥ð¥ð*) - S0 excitation. The conformational cooling during the supersonic expansion is found to be quite efficient in the Ar carrier gas giving the trans conformational isomer exclusively in the molecular beam, whereas both trans and cis conformers are populated in the jet when the sample is carried in Ne. Using the Stark deflector, trans and cis conformers are unambiguously identified, showing the distinct Stark deflection profiles according to their sufficiently different dipole moments of 1.013 or 1.670 Debye, respectively. For the trans conformer, the methyl moiety on the meta-position adopting the eclipsed geometry in S0 transforms into the staggered geometry in S1 to activate a series of the CH3 torsional mode. A Hamiltonian with the one-dimensional sinusoidal torsional potential is solved using the free-rotor basis set to explain the experiment, giving the three-fold torsional barrier of 34 and 304 cm-1 for S0 and S1, respectively. For the cis conformer, on the other hand, the CH3 torsion is little activated in the S1-S0 transition as both S0 and S1 adopt the staggered geometry at the minimum energy points. The doublet of each band of the cis conformer is ascribed to tunneling split due to the very low CH3 torsional barrier of 27 cm-1 in S0. It is found that the cis conformer undergoes the planar to pseudo-planar structural change upon the S1-S0 transition. Theoretical calculation based on the double-well model potential curve could explain the experiment quite well, suggesting that the SCH3 moiety of the cis conformer in S1 becomes out-ofplane with respect to the plane of the phenyl moiety. This implies that excited-state predissociation dynamics of trans and cis conformers of the title molecule might be different. |
|
[PDF] |
¢¹ Kyung Chul Woo and Sang Kyu Kim |
|
|
"Real-Time Observation of Fermi Resonances in the S1 State of Phenol"
J. Phys. Chem. Lett., 2020, 11 (1), pp 161-165
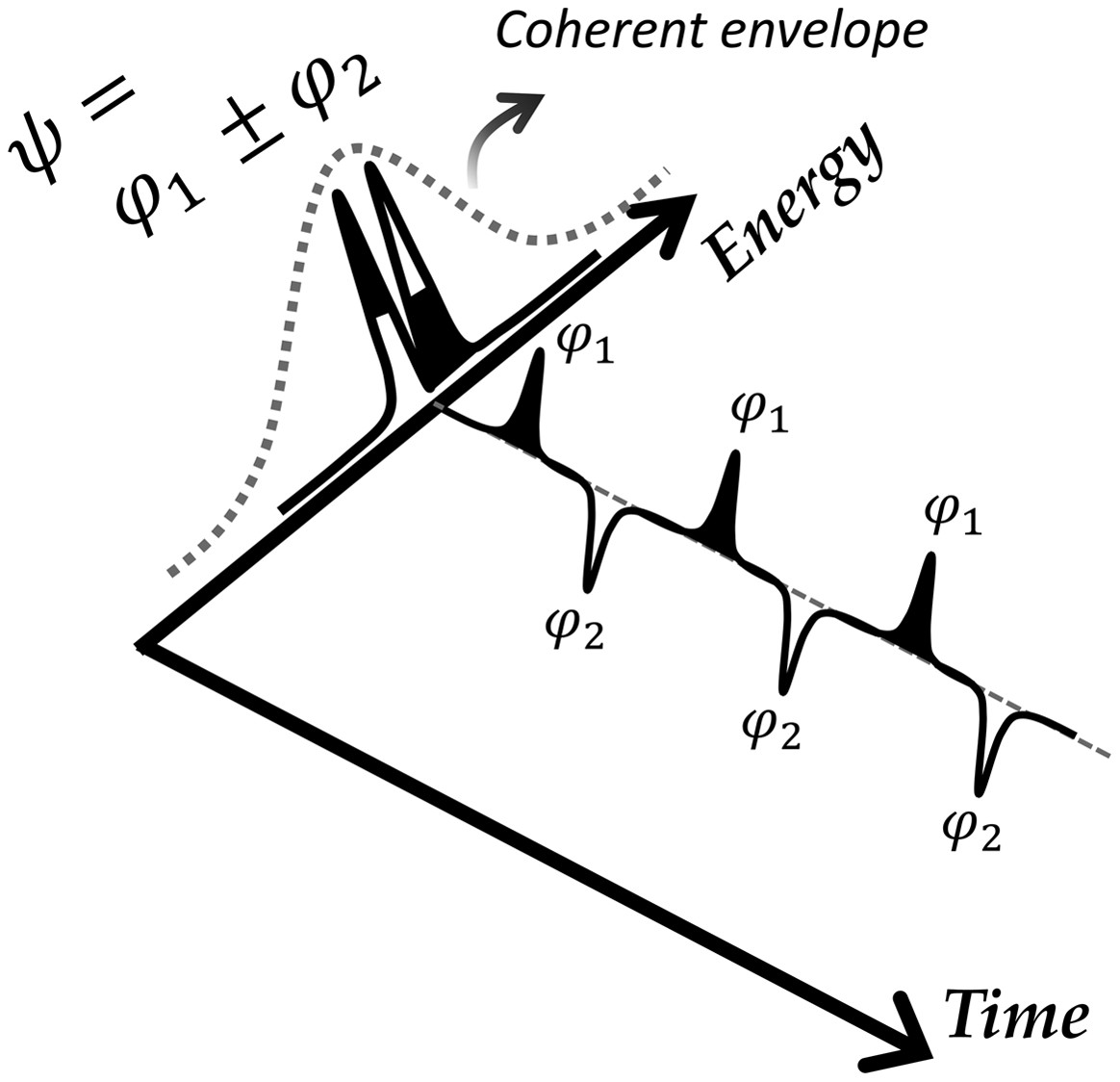
Fermi resonances in the first electronically excited (S1) state of phenol have been observed in real time. Quantum beats associated with coherent superposition of Fermi resonant eigenstates are manifested as temporal oscillations of the ionization cross sections of which the amplitudes are strongly dependent on the total ionization energy. This indicates that coherently excited eigenstates are effectively decomposed into their zeroth-order states, providing the unique opportunity for the investigation of nonstationary state dynamics in real-time. Energy gaps (¥Ä¥í?) of eigenstates within the laser coherence width have been most precisely determined up to date, giving ¥Ä¥í? ¡ 3.302 ¡¾ 0.001 or 1.655 ¡¾ 0.001 cm-1 for the 11/4110b1 or 122/8a1 Fermi doublets, respectively. Dephasing rate suddenly increases as the S1 internal energy becomes above ¡1500 cm-1, revealing the important role of energy randomization dynamics during the H atom tunneling process of phenol in S1. |
|
[PDF] |
|
|


|
¢¹ Jean Sun Lim, Hyun Sik You, So-Yeon Kim, Junggil Kim, Young Choon Park and Sang Kyu Kim |
|
|
"Vibronic Structure and Predissociation Dynamics of 2-methoxythiophenol (S1):
The Effect of Intramolecular Hydrogen Bonding on Nonadiabatic Dynamics"
J. Chem. Phys, 151, 244305 (2019)
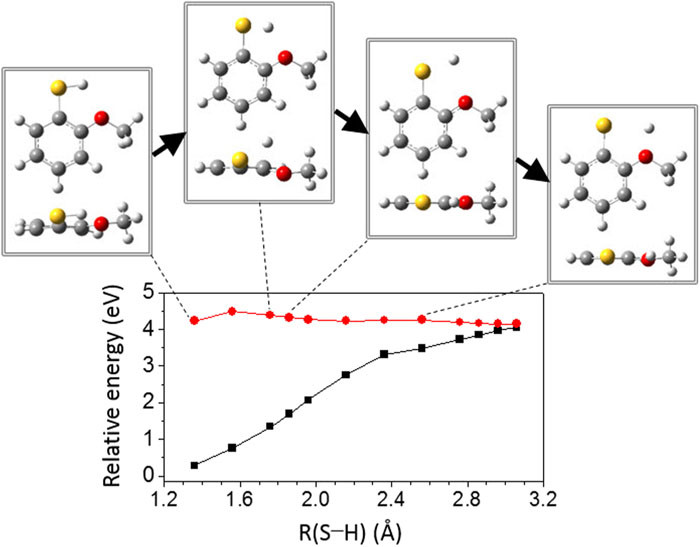
Vibronic spectroscopy and the S-H bond predissociation dynamics of 2-methoxythiophenol (2-MTP) in the S1 (¥ð¥ð*) state have been investigated for the first time. Resonant two-photon ionization and slow-electron velocity map imaging (SEVI) spectroscopies have revealed that the S1-S0 transition of 2-MTP is accompanied with the planar to the pseudoplanar structural change along the out-of-plane ring distortion and the tilt of the methoxy moiety. The S1 vibronic bands up to their internal energy of ¡1000 cm-1 are assigned from the SEVI spectra taken via various S1 vibronic intermediate states with the aid of ab initio calculations. Intriguingly, Fermi resonances have been identified for some vibronic bands. The S-H bond breakage of 2-MTP occurs via tunneling through an adiabatic barrier under the S1/S2 conical intersection seam, and it is followed by the bifurcation into either the adiabatic or nonadiabatic channel at the S0/S2 conical intersection where the diabatic S2 state (¥ð¥ò*) is unbound with respect to the S-H bond elongation coordinate, giving the excited (A) or ground ( ? X) state of the 2-methoxythiophenoxy radical, respectively. Surprisingly, the nonadiabatic transition probability at the S0/S2 conical intersection, estimated from the velocity map ion images of the nascent D fragment from 2-MTP-d1 (2-CH3O-C6H4SD) at the S1 zero-point energy level, is found to be exceptionally high to give the ?X/A product branching ratio of 2.03 ¡¾ 0.20, which is much higher than the value of ¡0.8 estimated for the bare thiophenol at the S1 origin. It even increases to 2.33 ¡¾ 0.17 at the ¥í452 mode (101 cm-1) before it rapidly decays to 0.69 ¡¾ 0.05 at the S1 internal energy of about 2200 cm-1. This suggests that the strong intramolecular hydrogen bonding of S···D···OCH3 in 2-MTP at least in the low S1 internal energy region should play a significant role in localizing the reactive flux onto the conical intersection seam. The minimum energy pathway calculations (second-order coupled-cluster resolution of the identity or time-dependent-density functional theory) of the adiabatic S1 state suggest that the intimate dynamic interplay between the S−H bond cleavage and intramolecular hydrogen bonding could be crucial in the nonadiabatic surface hopping dynamics taking place at the conical intersection. |
|
[PDF] |
¢¹ Jean Sun Lim, Hyun Sik You, Songhee Han and Sang Kyu Kim |
|
|
"Photodissociation dynamics of ortho-substituted thiophenol at 243 nm"
J. Phys. Chem. A, 2019, 123 (13), pp 2634-2639

The photoinduced S−H (D) bond fission dynamics of four ortho-substituted thiophenols, 2-fluoro, 2-chloro, 2-bromo, and 2-methoxythiophenol at a pump wavelength of 243 nm, have been investigated by velocity-map imaging and high-level electronic structure calculations. The D atom images of the deuterated ortho-substituted thiophenols show much reduced X?/A branching ratios of the cofragment radicals over that of bare thiophenol. The angular distributions of the D fragment display negative anisotropies, indicating that transition dipole moments are perpendicular to the fast dissociating S−D bond axis. Initial excitation at 243 nm occurs directly to the 1¥ð¥ò* state or to the 21¥ð¥ð* state followed by efficient coupling to the 1¥ð¥ò* state. The calculated potential energy curves for the 1¥ð¥ò* or 21¥ð¥ð* excited states of the ortho-substituted thiophenols along the CCS−D torsion angle (Φ) display minima at the nonplanar structures, whereas all of the states for bare thiophenol present minima at the planar geometries. This different topology of the ortho-substituted thiophenols in the excited states induces the wide spread of the reactive flux along the Φ coordinate on the repulsive surface as it should experience significant torque with respect to Φ during the fragmentation. This encourages the dissociating molecules to follow the adiabatic path at the conical intersection between the ground and the 1¥ð¥ò* states at extended S−D bond lengths, giving rise to decreased X?/A branching ratios, demonstrating that the excited-state molecular structure dictates the nonadiabatic transition probability. |
|
[PDF] |
¢¹ Kyung Chul Woo and Sang Kyu Kim |
|
|
"Mode-specific excited-state dynamics of N-methylpyrrole"
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2019, 21, 14387-14393
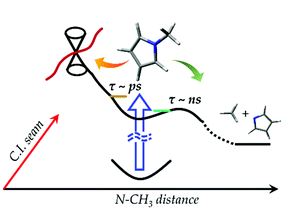
State-selective deactivation rates of N-methylpyrrole in the S1 state have been measured by using the picosecond pump?probe method. The S1 decay time leading to the N−CH3 bond dissociation is found to be strongly mode-dependent as manifested in both S1 decay and methyl-fragment growth dynamics. Time-resolved velocity-map ion images of the ¢«CH3 fragment, as far as the fragment of the Gaussian-shaped high kinetic energy distribution is concerned, suggest that the N−CH3 cleavage reaction might occur through an intermediate. Sudden decrease of the S1 lifetime at ¡700 cm-1 above the S1 origin is accompanied by the fragmentation of the Boltzmann-type low kinetic energy distribution. The appearance rate of this low-kinetic energy fragment turns out to be quite slow to give ¥ó ¡ 5 ns compared to the S1 lifetime of ¡174 ps at the +806 cm-1 band, for instance, confirming previous findings that the S1 decay process starts to be overwhelmed by a new fast nonradiative transition in the corresponding excitation energy region. The lifetime at the S1 origin accessed by the two-photon absorption is firstly measured to give ¥ó ¡ 8 ns. Using one and two photon absoption processes, a number of S1 vibronic bands are identified to give mode-dependent lifetimes spanning an enormously wide temporal range of 8 ns-5 ps in the quite narrow excitation energy region of 0-1800 cm-1 above the S1 origin. Understanding of the N-methylpyrrole dynamics on multidimensional excited-state potential energy surfaces governing energy dissipating processes will get much benefit from our detailed mode-specific lifetime measurements. |
|
[PDF] |
¢¹ Kyung Chul Woo and Sang Kyu Kim |
|
|
"Multidimensional H-Atom Tunneling Dynamics of Phenol:
Interplay between Vibrations and Tunneling"
J. Phys. Chem. A, 2019, 123 (8), pp 1529-1537
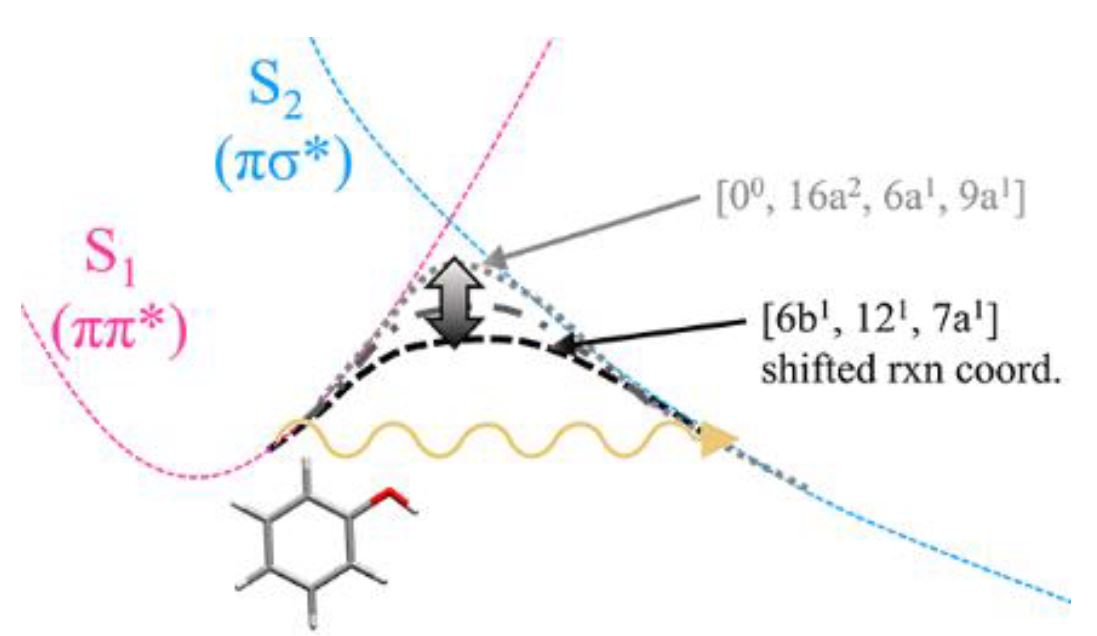
Multi-dimensional facets of the hydrogen tunneling dynamics of phenol excited in S1 (¥ð¥ò*) have been unraveled to give particular S1 vibronic states strongly coupled or actively decoupled to the O−H tunneling coordinate. Strong mode-dependent variation of the tunneling rate measured with picosecond lasers indicates that tunneling probability is extremely sensitive to low-frequency vibrational modes seemingly orthogonal to the O−H elongation coordinate unless the rate of energy randomization exceeds that of tunneling. The multi-dimensional nature of tunneling has also been manifested in efficient internal-to-translational energy transfers observed at S1 vibronic modes strongly coupled to the tunneling coordinate, giving insights into otherwise the formidable multidimensional map of tunneling process. The nonadiabatic bifurcation dynamics in the later stage of the chemical reaction has been disentangled by analyzing picosecond time-resolved product state distributions, resolving a long controversial issue regarding the origin of high or low kinetic energy component of the product translational energy distributions.
|
|
[PDF] |
¢¹ Jean Sun Lim, Hyun Sik You, So-Yeon Kim and Sang Kyu Kim |
|
|
"Experimental Observation of Nonadiabatic Bifurcation Dynamics
at Resonances in the Continuum"
Chem. Sci., 2019, 10, 2404-2412
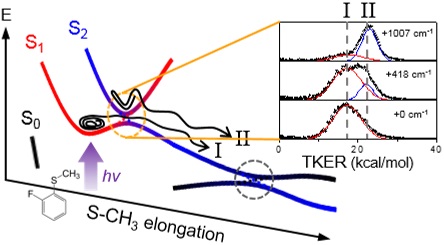
The surface crossing of bound and unbound electronic states in multidimensional space often gives rise to resonances in the continuum. This situation happens in the ¥ð¥ò*-mediated photodissociation reaction of 2-fluorothioanisole; optically-bright bound S1 (¥ð¥ð*) vibrational states of 2-fluorothioanisole are strongly coupled to the optically-dark S2 (¥ð¥ò*) state, which is repulsive along the S−CH3 elongation coordinate. It is revealed here that the reactive flux prepared at such resonances in the continuum bifurcates into two distinct reaction pathways with totally different dynamics in terms of energy disposal and nonadiabatic transition probability. This indicates that the reactive flux in the Franck-Condon region may either undergo nonadiabatic transition funneling through the conical intersection from the upper adiabat, or follow a low-lying adiabatic path, along which multiple dynamic saddle points may be located. Since 2-fluorothioanisole adopts a nonplanar geometry in the S1 minimum energy, the quasi-degenerate S1/S2 crossing seam in the nonplanar geometry, which lies well below the planar S1/S2 conical intersection, is likely responsible for the efficient vibronic coupling, especially in the low S1 internal energy region. As the excitation energy increases, bound-to-continuum coupling is facilitated with the aid of intramolecular vibrational redistribution, along many degrees of freedom spanning the large structural volume. This leads to the rapid domination of the continuum character of the reactive flux. This work reports direct and robust experimental observations of the nonadiabatic bifurcation dynamics of the reactive flux occurring at resonances in the continuum of polyatomic molecules. |
|
[PDF] |
|
|


|
¢¹ Hyun Sik You, Junggil Kim, Songhee Han, Doo-Sik Ahn, Jean Sun Lim and Sang Kyu Kim |
|
|
"Spatial Isolation of Conformational Isomers of Hydroquinone and
Its Water Cluster Using the Stark Deflector"
J. Phys. Chem. A, 122, 5, 1194-1199
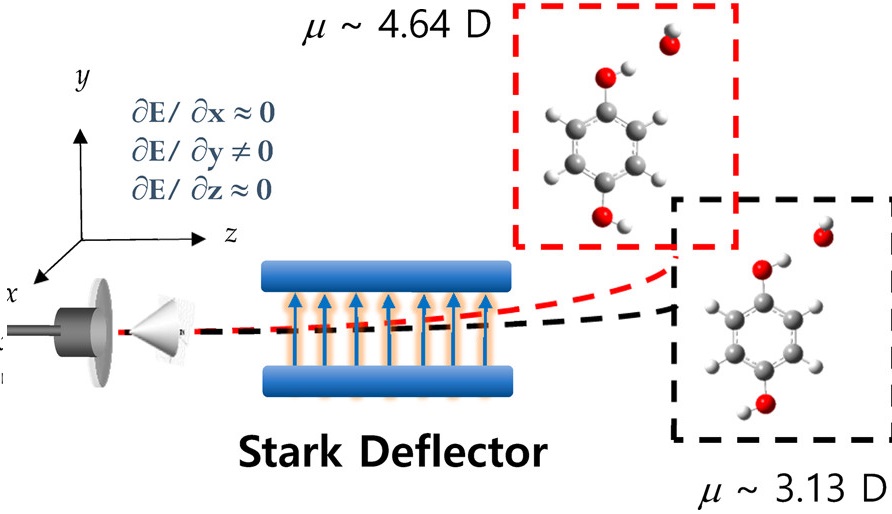
Conformational isomers of hydroquinone and their 1:1 clusters with water have been spatially separated using a Stark deflector in a supersonic jet. trans-Hydroquinone (HyQ) conformer with zero dipole moment is little influenced by inhomogeneous electric fields, whereas cis conformer with nonzero dipole moment (2.38 D) is significantly deflected from the molecular beam axis into the direction along which the strong field gradient is applied. Resonant two photon ionization carried out by shifting the laser position perpendicular to the molecular beam axis after the Stark deflector then gives an exclusive S1?S0 excitation spectrum of the cis conformer only, making possible immaculate conformer-specific spectroscopy and dynamics. As the spatial separation is apparently proportional to the effective dipole moment strength, conformational assignment could be absolute in the Stark deflector, which contrasts with the hole-burning spectroscopic technique where identification of a conformational isomer is intrinsically not unambiguous. trans- and cis-HyQ?H2O clusters have also been spatially separated according to their distinct effective dipole moment strengths to give absolute spectroscopic identification of each cluster isomer, nailing down the otherwise disputable conformational assignment. This is the first report for the spatial separation of conformational cluster isomers.. |
|
[PDF] |
|
|


|
¢¹ Dahyi Jeong, Dong-gu Kang, Taiha Joo, and Sang Kyu Kim |
|
|
"Femtosecond-Resolved Excited State Relaxation Dynamics
of Copper (II) Tetraphenylporphyrin (CuTPP) After Soret Band Excitation"
Sci. Rep., 7, 16865 (2017)

Excited state relaxation dynamics of Copper (II) tetraphenylporphyrin (CuTPP) after Soret band excitation have been investigated in various solvents by femtosecond broadband transient absorption spectroscopy. Signifcant role of charge transfer state has been confrmed from fast relaxation of triplet CuTPP in pyridine, giving τ~26.5ps. In piperidine, the transient measured at 480nm shows biexponential behavior with distinct time constants of 300 fs and 27.4ps. The fast component with τ~300 fs is attributed to relaxation of the CuTPP-piperidine adduct populated in the ground state, giving the intrinsic relaxation rate of the CuTPP exciplex for the frst time. For CuTPP in O-coordinating solvents of 1,4-dioxane and tetrahydrofuran (THF), a completely new relaxation channel via the 2[dz2, dx2−;y2] state is opened. As the exciplex formation is difusion controlled, triplet CuTPP lifetimes in pure solvents employed here are all measured to be more or less same to give ~30ps, whereas the 2[dz2, dx2−y2] exciplex formed by the ligation with O-coordinating solvents is found to relax much slowly to the ground state, giving lifetimes of ~360 and ~270ps in 1,4-dioxane and THF, respectively. |
|
[PDF] |
¢¹ Kyung Chul Woo, Do Hyung Kang, and Sang Kyu Kim |
|
|
"Real-Time Observation of Nonadiabatic Bifurcation Dynamics
at a Conical Intersection"
J. Am. Chem. Soc., 139 (47), 17152-17158 (2017)
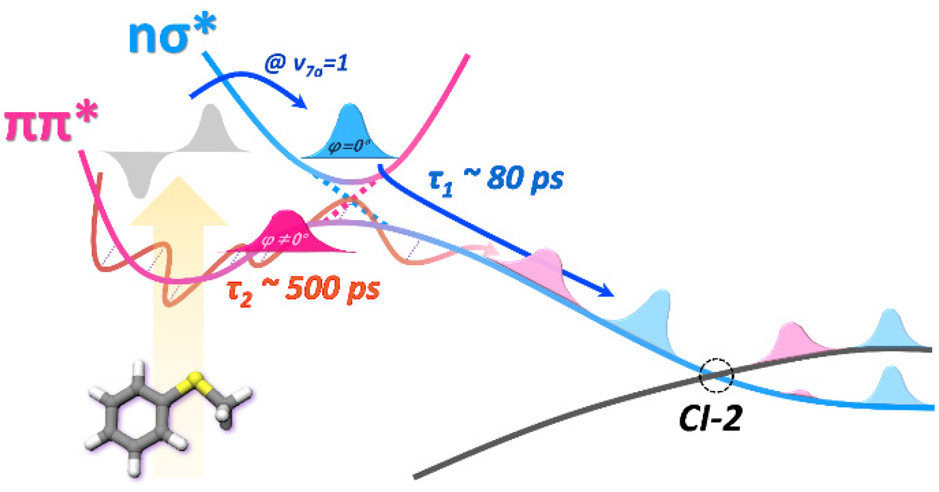
Looking into temporal dynamics of the reactive flux that is precisely located at the well-characterized conical intersection has been one of chemists’ longstanding goals. We report here real-time nonadiabatic bifurcation dynamics in the S–CH3 bond predissociation of thioanisole (C6H5SCH3) in the first electronically excited state (S1). It is found that two distinct adiabatic and nonadiabatic reaction pathways are activated simultaneously only when the vibronic state near the first conical intersection is optically accessed. Our time-resolved measurement of the product state distribution could separate two different dynamic channels unambiguously, unraveling the detailed dynamic mechanism of the nonadiabatic reaction taking place in the vicinity of the conical intersection. The nonadiabatic channel, where the reactive flux funnels through two consecutive conical intersections along the reaction coordinate, is found to be significantly faster than the adiabatic channel along the minimum energy reaction pathway. The kinetic energy release ratio and the nonadiabatic transition probability are found to be much higher for the nonadiabatic channel than those of the adiabatic channel, giving insights into the bifurcation dynamics occurring at the conical intersection. |
|
[PDF] |
¢¹ Ji Yong Choi, Dahyi Jeong, Seon Joo Lee, Dong-gu Kang, Sang Kyu Kim, Ki Min Nam and Hyunjoon Song |
|
|
"Engineering Reaction Kinetics by Tailoring the Metal tips of
Metal-Semiconductor Nanodumbbells"
Nano Lett., 17 (9), 5688-5694 (2017)
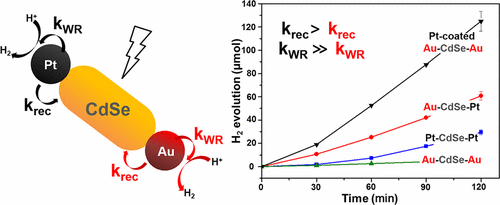
Semiconductor–metal hybrid nanostructures are one of the best model catalysts for understanding photocatalytic hydrogen generation. To investigate the optimal structure of metal cocatalysts, metal–CdSe–metal nanodumbbells were synthesized with three distinct sets of metal tips, Pt–CdSe–Pt, Au–CdSe–Au, and Au–CdSe–Pt. Photoelectrochemical responses and transient absorption spectra showed that the competition between the charge recombination at the metal–CdSe interface and the water reduction on the metal surface is a detrimental factor for the apparent hydrogen evolution rate. For instance, a large recombination rate (krec) at the Pt–CdSe interface limits the quantum yield of hydrogen generation despite a superior water reduction rate (kWR) on the Pt surface. To suppress the recombination process, Pt was selectively deposited onto the Au tips of Au–CdSe–Au nanodumbbells in which the krec was diminished at the Au–CdSe interface, and the large kWR was maintained on the Pt surface. As a result, the optimal structure of the Pt-coated Au–CdSe–Au nanodumbbells reached a quantum yield of 4.84%. These findings successfully demonstrate that the rational design of a metal cocatalyst and metal–semiconductor interface can additionally enhance the catalytic performance of the photochemical hydrogen generation reactions. |
|
[PDF] |
|
¢¹ So-Yeon Kim, Jeongmook Lee, and Sang Kyu Kim |
|
|
"Conformer Specific Nonadiabatic Reaction Dynamics in
Photodissocaition of Partially Deutrated Thioanisoles
(C6H5S-CH2D and C6H5S-CHD2)"
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 19, 18902-18912 (2017)

In this work, we have investigated nonadiabatic dynamics in the vicinity of conical intersections for predissociation reactions of partially deuterated thioanisole molecules; C6H5S-CH2D and C6H5S-CHD2. Each isotopomer has two distinct rotational conformers according to the geometrical position of D or H of the methyl moiety with respect to the molecular plane for C6H5S-CH2D or C6H5S-CHD2, respectively, as spectroscopically characterized in our earlier report [J. Phys. Chem. A, 118, 1850 (2014)]. Since identification and separation of two different rotational conformers of each isotopomer have been unambiguously done, we could interrogate nonadiabatic dynamics of thioanisole in terms of both H/D substitutional and conformational structural effects. Nonadiabatic transition probability, estimated by the experimentally measured branching ratio of the nonadiabatically produced ground-state channel giving C6H5S(X) versus the adiabatic excited-state channel leading to the C6H5S(A) radical, shows resonance-like increases at symmetric (vS) or asymmetric (7a) S-CH2D (or S-CHD2) stretching mode excitation in S1 for all conformational isomers of two isotopomers. However, absolute probabilistic value of the nonadiabatic transition is found to vary quite drastically depending on different conformers and isotopomers. Experimental finding here that nonadiabatic transition dynamics are very sensitive to subtle changes in the nuclear configuration within the Franck-Condon region induced by the H/D substitution indicates that the S1/S2 conical intersection seam is quite narrowly defined in the multi-dimensional nuclear configurational space as far as the S-methyl predissociation reaction is concerned. In order to understand the relation between molecular structure and nonadiabaticity of reaction, potential energy surfaces near S1/S2 conical intersections have been theoretically calculated along vS and 7a normal mode coordinates for all conformational isomers. Slow-electron velocity map imaging (SEVI) spectroscopy is employed to unravel the extent of intramolecular vibrational redistribution (IVR) for particular mode excitations of S1, giving insights into dynamic interplay between IVR and nonadiabatic transition probability near the conical intersection seam.
|
|
|
[PDF]
|
|
|

|
¢¹ So-Yeon Kim, Jeongmook Lee, and Sang Kyu Kim, Young S. Choi |
|
|
"Nonplanar structure of C6H5SCF3 facilitates πσ*-mediated
photodissociation reaction on the S1 state"
Chemical Physics Letters, 659, 43-47 (2016)
Vibrational structure of trifluoromethylthiobenzene (C6H5SCF3) on the S1 state has been investigated by resonance-enhanced two-photon ionization spectroscopy and nature of predissociation dynamics is inferred from homogeneously broadened spectral features. As (C6H5SCF3) adopts a nonplanar structure in both the S0 and S1 states, the effective adiabatic barrier generated by avoided crossing of opticallybright bound S1 (ππ*) and dark-repulsive S2 (πσ*) surfaces along the reaction coordinate is significantly lowered, giving the S1 lifetime of ~300 fs. This experiment demonstrates that the molecular structure spanned by the reactive flux near the curve-crossing region dictates reaction rate as well as nonadiabatic transition probability. |
|
[PDF] |
|
|


|
¢¹ So-Yeon Kim, Jeongmook Lee, and Sang Kyu Kim |
|
|
"H/D Substitution Makes Difference in Photochemical Studies:
the Case of Dimethylamine"
Rapid Communication in Photoscience, 4, 3, 63-66 (2015)
When the molecule in the excited state is subject to prompt predissociation, it is quite nontrivial to obtain vibrational structure of the excited state in general. This applies to the case of photochemistry of dimethylamine (DMA:(CH3)2NH). When DMA is excited to its first electronically excited state (S1), the N-H bond dissociation occurs promptly. Therefore, S1 vibronic bands are homogeneously broadened to give extremely small ionization cross sections and heavily-congested spectral features, making infeasible any reasonable spectral assignment. Here, we demonstrate that the predissociation rate of the excited state could be significantly reduced by the NH/ND substitution to give the much better-resolved S1 spectral feature, revealing the vibrational structure of the excited state of DMA-d1 ((CH3)2ND) for the first time. |
|
[PDF] |
¢¹ Hyun Sik You, Songhee Han, Jun-Ho Yoon, Jeong Sik Lim, Jeongmook Lee,
So-Yeon Kim, Doo-Sik Ahn, Jean Sun Lim, and Sang Kyu Kim |
|
|
"Structure and Dynamic Role of Conical Intersections
in the πσ*-mediated Photodissociation Reactions"
International Reviews in Physical Chemistry, 34, 3, 429-459 (2015)
Conical intersection as a dynamic funnel in nonadiabatic transition dictates many important chemical reaction outputs such as reaction rates, yields, and energy disposals especially for chemical reactions taking place on electronically excited states. Therefore, the energetics and topology of conical intersections have been subjected to intensive theoretical and experimental studies for decades as these things are the keys to understanding and controlling nonadiabatic transitions which are ubiquitous in nature. In this article, we focus on πσ*-mediated photodissociation reactions of thiophenols and thioanisoles. Interestingly, for these chemical systems, the nonadiabatic transition probability can be precisely measured as a function of the excitation energy, giving a great opportunity for spectroscopic characterization of the multi-dimensional conical intersection seam that governs the nonadiabatic transition dynamics of polyatomic molecules. The passage of the reactive flux in the proximity of the conical intersection gives rise to dynamic resonances corresponding to dramatic state-specific increases of the nonadiabatic transition probability. Accordingly, it is found that the electronic and nuclear configurations of the reactive flux and their evolution, coupled to the conical intersection seam, are critical in nonadiabatic transition dynamics. Nonadiabaticity is found to be extremely sensitive to the conformational molecular structure, and this has been demonstrated in the photodissociation dynamics of the chemical derivatives of thiophenol. Intramolecular vibrational redistribution, which is nontrivial in surmounting the reaction barrier, is found to wash out state-specific dynamic resonances, implying the importance of the dynamic interplay between vibrational energy flow and nonadiabatic transition. The experimental results on conical intersection dynamics presented in this review provide many interesting and important issues to be pursued in the near future by both theoreticians and experimentalists. |
|
[PDF]
|
|
¢¹ Hyun Sik You, Songhee Han, Jean Sun Lim, and Sang Kyu Kim
|
|
|
|
"(¥ð¥ð*/¥ð¥ò*) Conical Intersection Seam Experimentally Observed
in the S–D Bond Dissociation Reaction of Thiophenol-d1"
J. Phys. Chem. Lett., 6, 3202-3208 (2015)

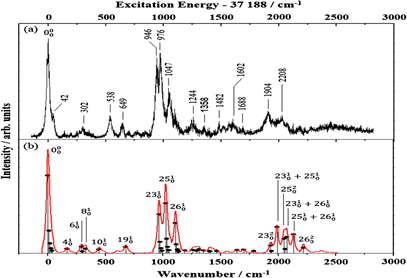
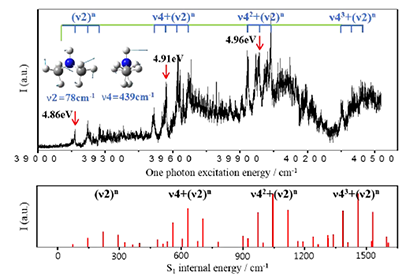
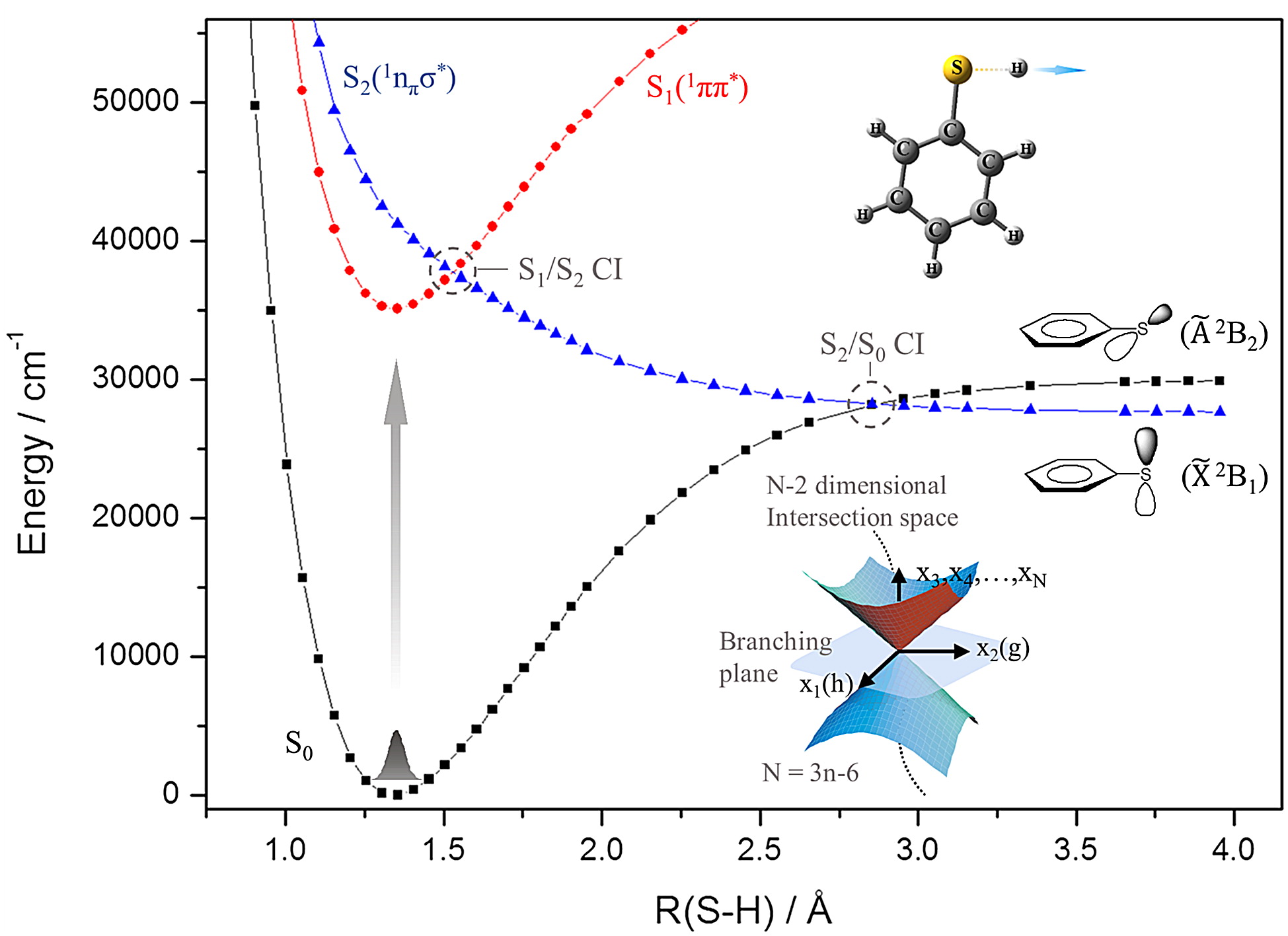
Surface crossing of bound (S1, ¥ð¥ð*) and continuum (S2, ¥ð¥ò*) states has been observed in the ultrafast S–D bond dissociation reaction of thiophenol-d1. It is manifested by an unanticipated variation of fragment angular distribution as a function of the excitation energy. The anisotropy parameter (¥â) of +0.25 at the S1 origin decreases to -0.60 at ¡600 cm–1 above the S1 zero-point level, giving a broad peak in ¥â with a bandwidth of ¡200 cm–1. The peak in ¥â is ascribed to the in-plane S-D bending mode excitation by which the nuclear configuration in the proximity of the S1/S2 conical intersection seam is directly accessed, showing a mixed character of parallel (S1–S0) and perpendicular (S2–S0) transition dipole moments at the same time. As a result, the dynamic aspect of the conical intersection is experimentally revealed here through direct access to the nuclear configuration on the multidimensional conical intersection seam.
|
|
|
[PDF]
|
|
|


|
|
¢¹ Songhee Han, Hyun Sik You, So-Yeon Kim, and Sang Kyu Kim
|
|
|
|
"Dynamic Role of the Intramolecular Hydrogen Bonding in Nonadiabatic Chemistry
Revealed in the UV Photodissociation Reactions of 2-Fluorothiophenol and 2-Chlorothiophenol"
J. Phys. Chem. A, 118, 6940-6949 (2014)
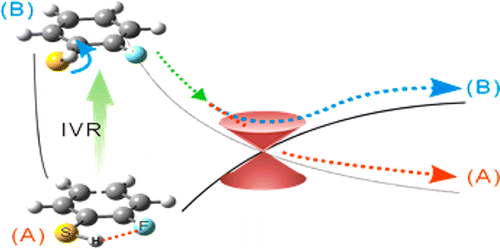
The dynamic interplay between the intramolecular hydrogen bonding and intramolecular vibrational redistribution is found to be critical in nonadiabatic reaction dynamics. Herein, it has been demonstrated that the molecular planarity, directed by the intramolecular hydrogen bonding, plays an important role in the nonadiabatic passage of the reactive flux at the conical intersection in the photodissociation reactions of 2-fluorothiophenol and 2-chlorothiophenol. As the internal energy increases in the excited state, the intramolecular hydrogen bonding of 2-fluorothiophenol loosens. The floppiness brought into the molecular structure then modifies the dynamic path of the reactive flux, leading to the diminishment of the nonadiabatic transition probability at the conical intersection. On the contrary, for 2-chlorothiophenol having the relatively stronger intramolecular hydrogen bonding, the reactive flux seems to retain the molecular planarity even with the increase of the internal energy as manifested by the constant nonadiabatic transition probability over the wide range of the S1 internal energy. The effect of the intramolecular hydrogen bonding on the molecular structure and its relation to the nonadiabatic dynamics along the tunneling path has been experimentally demonstrated.
|
|
|
[PDF]
|
|
¢¹ Dahyi Jeong, Ki Young Yeon, and Sang Kyu Kim
|
|
|
|
"Tip-enhanced Electron Emission Microscopy Coupled with the Femtosecond Laser Pulse"
Bull. Korean Chem. Soc., 35, 891 (2014)
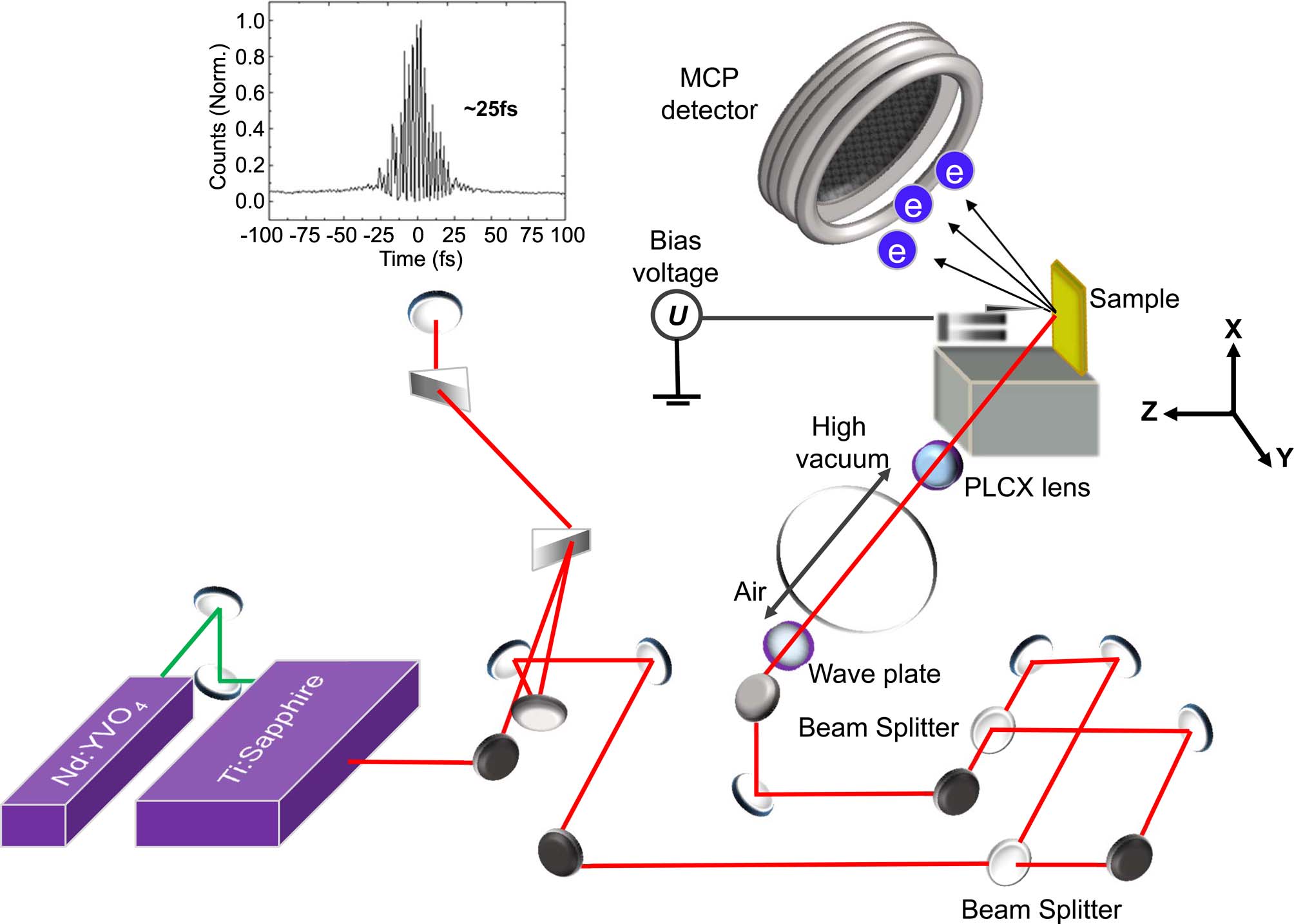
The ultrashort electron pulse, laser-emitted from the metal tip apex has been characterized and used as a probing source for a new electron microscope to visualize the morphology of the gold-mesh in the nanometric resolution. As the gap between the tungsten tip and Au-surface is approached within a few nm, the large electromagnetic field enhancement for the incident P-polarized laser pulse with respect to the tip-sample axis is strongly observed. Here, we demonstrate that the time-resolved tip-enhanced electron emission microscope (TEEM) can be implemented on the laboratory table top to give the two-dimensional image, opening lots of challenges and opportunities in the near future.
|
|
|
[PDF]
|
|
¢¹ Jun-Ho Yoon, Kyung Chul Woo, and Sang Kyu Kim
|
|
|
|
"Vibronic Structures and Dynamics of the Predissociating Dimethyl Sulfide
and its Isotopomers (CH3SCH3, CD3SCD3, CH3SCD3) at the Conical Intersection"
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 16, 8949-8955 (2014)
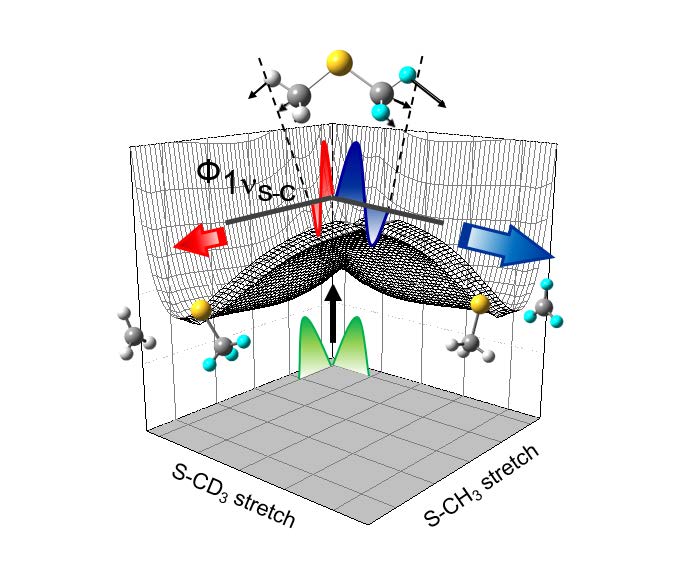
Conical intersection seam comprised of crossing surfaces of two lowest excited states of dimethyl sulfide (DMS) has been directly accessed by the one-photon excitation from the ground equilibrium state. Since the S-C bond rupture takes place promptly, the molecular structure on the excited state effectively belongs to CS symmetry. Namely, excited states of 11B1 and 11A2 in C2V become 11A¡Ç and 21A¡Ç states in CS, respectively, and the optical transition from the ground equilibrium state to the dissociating molecule at the conical intersection seam is symmetry-allowed to facilitate the nonadiabatic transition on the 21A¡Ç state, leading eventually to the CH3S + CH3 products. The dynamic study of DMS, in this sense, gives the great opportunity to unravel the vibronic structure of the conical intersection seam by the conventional one-photon excitation method. In this work, utilizing the photofragment excitation (PHOFEX) spectroscopic method, the vibronic structures of DMS and its isotope analogs (CD3SCD3, CH3SCD3) at the conical intersection seam have been revealed, providing accurate lifetimes and detailed dynamics associated with individual vibronic transitions. Lifetime of the excited DMS is estimated to be ~ 100 fs, indicating that the dissociation is complete within one single oscillation in the conical intersection region. It is also found that the symmetric CSC stretching mode is strongly coupled to the reaction coordinate, as manifested by our experimental finding that the fragmentation yield of the S-CD3 bond is enhanced compared to that of the S-CH3 bond in the CH3SCD3 dissociation reaction only when the CSC symmetric stretching vibrational mode is excited at the conical intersection region. This work demonstrates that the better understanding of the excited state could make the bond-selective chemistry into reality.
|
|
|
[PDF]
|
|
¢¹ Jeongmook Lee, So-Yeon Kim, and Sang Kyu Kim
|
|
|
|
"Spectroscopic Separation of the Methyl Internal Rotational Isomers
of Thioanisole Isotopomers (C6H5S-CH2D and C6H5S-CHD2)"
J. Phys. Chem. A, 118, 1850 (2014)
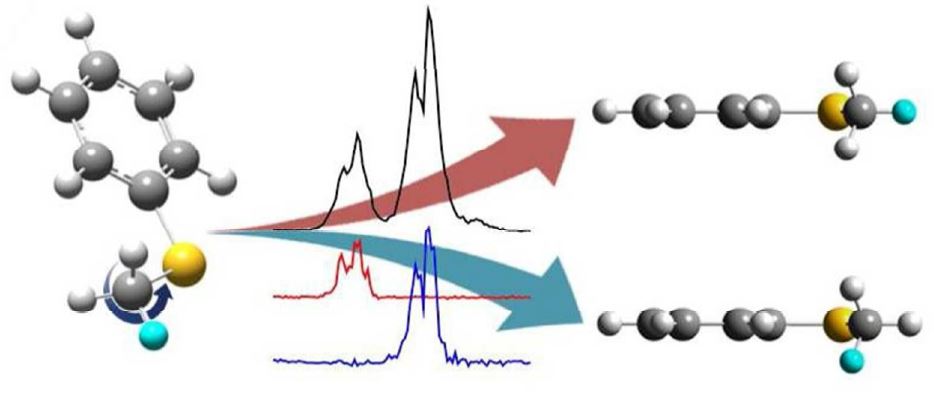
Two distinct rotational isomers of thioanisole-d1 (C6H5S-CH2D) and thioanisole-d2 (C6H5S-CHD2) with respect to the internal rotation of the methyl moiety have been identified and characterized spectroscopically using the resonantly-enhanced two photon ionization (R2PI), UV-UV hole burning, and slow-electron velocity map imaging (SEVI) techniques. From the statistical weights, the definite assignment for the specific rotational isomer of each isotopomer has been successfully done, providing isomer-specific ionization energies and vibrational frequencies of S1/D0 states. Detailed molecular structures, the methyl internal-rotor barrier, and normal mode descriptions for selective vibrations are discussed with the aid of density functional theory calculations.
|
|
|
[PDF]
|
|
¢¹ Songhee Han, Jeong Sik Lim, Jun-Ho Yoon, Jeongmook Lee, So-Yeon Kim,
and Sang Kyu Kim
|
|
|
|
"Conical Intersection Seam and Bound Resonances Embedded in Continuum
Observed in the Photodissociation of Thioanisole-d3"
J. Chem. Phys., 140, 054307 (2014)
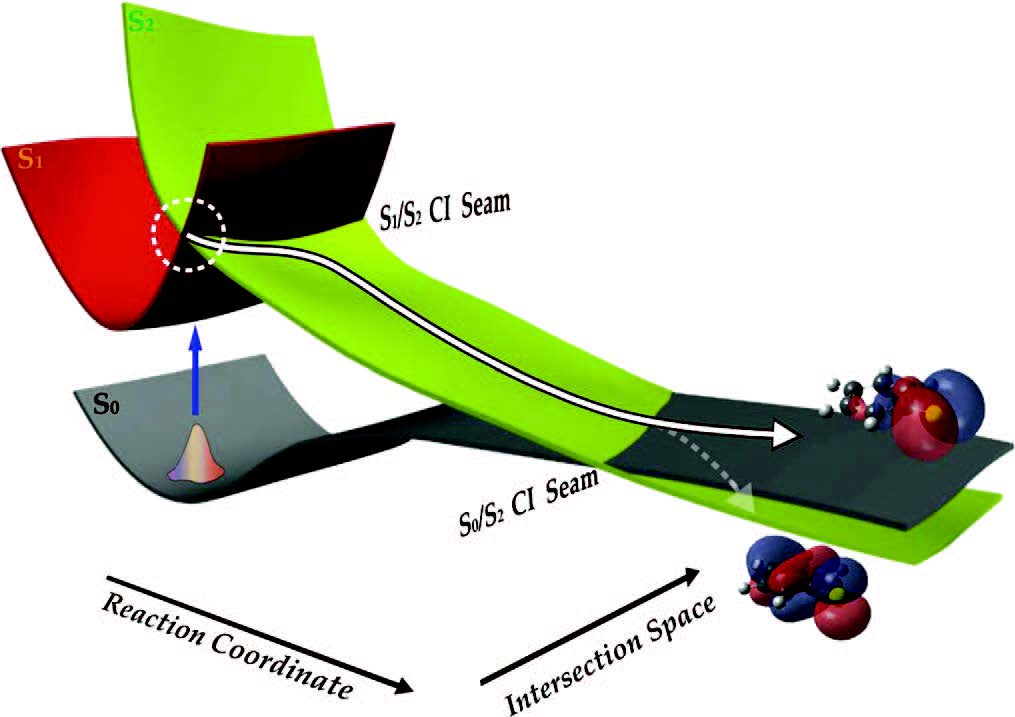
Herein, the multi-dimensional nature of the conical intersection seam has been experimentally revealed in the photodissociation reaction of thioanisole-d3 (C6H5SCD3) excited on S1, giving C6H5S· (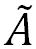 or or 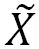 ) + ·CD3 products. The translational energy distribution of the nascent ·CD3 fragment, reflecting the relative yields of the C6H5S· ( ) + ·CD3 products. The translational energy distribution of the nascent ·CD3 fragment, reflecting the relative yields of the C6H5S· (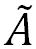 ) and C6H5S· ( ) and C6H5S· (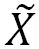 ) products, was measured at each S1 vibronic band using the velocity map ion imaging technique. Direct access of the reactant flux to the conical intersection seam leads to the increase of the nonadiabatic transition probability resulting in sharp resonances in the ) products, was measured at each S1 vibronic band using the velocity map ion imaging technique. Direct access of the reactant flux to the conical intersection seam leads to the increase of the nonadiabatic transition probability resulting in sharp resonances in the 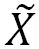 / /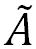 C6H5S· product branching ratio at several distinct S1 vibronic bands. The nature of the S1 vibronic bands associated with such dynamic resonances was clarified by the mass-analyzed threshold ionization spectroscopy. The bound state embedded in continuum generated by the conical intersection is observed as a distinct dynamic resonance, revealing the nature of the nuclear motion responsible for the nonadiabatic coupling of two potential energy surfaces at the conical intersection. The multi-dimensional facets of the conical intersection seam in terms of its detailed structure and dynamic role are discussed with the aid of theoretical calculations. C6H5S· product branching ratio at several distinct S1 vibronic bands. The nature of the S1 vibronic bands associated with such dynamic resonances was clarified by the mass-analyzed threshold ionization spectroscopy. The bound state embedded in continuum generated by the conical intersection is observed as a distinct dynamic resonance, revealing the nature of the nuclear motion responsible for the nonadiabatic coupling of two potential energy surfaces at the conical intersection. The multi-dimensional facets of the conical intersection seam in terms of its detailed structure and dynamic role are discussed with the aid of theoretical calculations.
|
|
|
[PDF]
|
|
|

|
|
¢¹ Jeongmook Lee, So-Yeon Kim, and Sang Kyu Kim
|
|
|
|
"Spectroscopic Study on Nonradiative Transition and Ionization of
5-methylpyrimidine at S1 Probed by the Slow-electron Velocity-map Imaging (SEVI) Technique"
Chem. Phys. Lett., 568, 36 (2013)
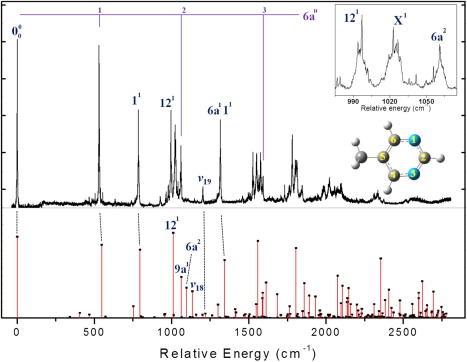
Slow electron velocity-map imaging (SEVI) has been employed for the ionization spectroscopic study of the jet-cooled 5-methylpyrimidine in the first singlet 1(n¥ð*) excited state. Resonant-enhanced two-color two-photon (1+1¡¯) ionization spectrum gives well-resolved S1 vibrational structures up to ~ 2400 cm-1 above the origin whereas spectral bands becomes completely broadened in the higher energy region as coupling of individual S1 bands to dark states becomes significant. Ionization of the S1 5-methylpyrimidine with different ionization wavelengths at several different delay times reveals the property of low-lying 3(¥ð¥ð*) triplet dark state which is prepared by fast nonadiabatic transition. SEVI spectra taken via various S1 intermediate states provide the detailed vibrational structures of the 5-methylpyrimidine cation (D0), also giving the adiabatic ionization energy of 9.1052 ± 0.0030 eV (73 438 ± 24 cm-1). Geometrical changes in the S0-S1-D0 transitions are discussed from Franck-Condon simulations based on calculations by (time-dependent) density functional theory.
|
|
|
[PDF]
|
|
¢¹ Jeongmook Lee, Doo-Sik Ahn, and Sang Kyu Kim
|
|
|
|
"Valence Electron Ionization Dynamics of Chromium by a Photoelectron Imaging Technique:
J+ -Dependent State and Angular Distribution"
J. Phys. Chem. A, 117, 2138 (2013)

The photoionization of Cr at excited states is investigated using a velocity-map photoelectron imaging technique. Benzene chromium carbonyl or bis(¥ç6- benzene) chromium was used as a precursor for the generation of excited Cr atoms. The a5S2 ¡æ x5P°3 and a5D3 ¡æ y5D°2 transitions are then employed for the preparation of resonant intermediate states in a two-color two-photon ionization process, in which an electronic configurational change from 3d4(5D)4s4p(1P°) to 3d44s(6DJ+) occurs. The photo- electron kinetic energy distribution is found to be very sensitive to the ionization energy and the total angular momentum quantum number of the chromium ion (J+). Anisotropy parameters associated with departing electrons also show significant variation depending on the energy and total angular momentum quantum number, suggesting that direct and/or indirect ionization should be quantum-mechanically mixed, manifesting the complicated nature of angular momentum couplings in the ionization continuum.
|
|
|
[PDF]
|
|
¢¹ Jun-Ho Yoon, Jeong Sik Lim, Kyung Chul Woo, Myung Soo Kim, and Sang Kyu Kim
|
|
|
|
"Chemical Substitution Effect on Energetic and Structural Differences between
Ground and First Electronically Excited States of Thiophenoxyl Radicals"
Bull. Korean Chem. Soc., 34, 415 (2013)
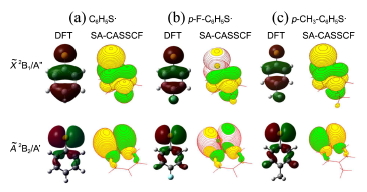
Effect of chemical substitution at the para-position of the thiophenoxyl radical has been theoretically investigated in terms of energetics, structures, charge densities and orbital shapes for the ground and first electronically excited states. It is found that the adiabatic energy gap increases when CH3 or F is substituted at the para-position. This change is attributed to the stabilization of the ground state of thiophenoxyl radical through the electron-donating effect of F or CH3 group as the charge or spin of the singly-occupied molecular orbital is delocalized over the entire molecule especially in the ground state whereas in the excited state it is rather localized on sulfur and little affected by chemical substitutions. Quantitative comparison of predictions based on four different quantum-mechanical calculation methods is presented.
|
|
|
[PDF]
|
|
|


|
|
¢¹ Doo-Sik Ahn, Jeongmook Lee, Young Choon Park, Yoon Sup Lee, and Sang Kyu Kim
|
|
|
|
"Nuclear motion Captured by the slow electron velocity imaging technique
in the tunnelling predissociation of the S1 methylamines"
J. Chem. Phys., 136, 024306 (2012)
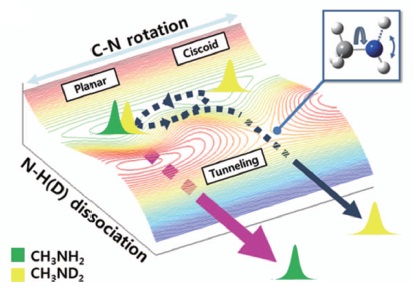
Predissociation dynamics of methylamines (CH3NH2 and CH3ND2) on the first electronically excitedstates are studied using the slow-electron velocity imaging method to unravel the multi-dimensional nature of the N–H(D) chemical bond dissociation reaction which occurs via tunnelling. The nearly free internal rotation around the C–N bond axis is found to be strongly coupled to the reaction pathway, revealing nuclear motions actively involved in the tunnelling process on the S1 potential energy surfaces. The vibrational state-resolved energy and angular distributions of photoelectron, ejected from the ionization mediated by the metastable intermediate S1 state provide a unique way for mapping the predissociative potential energy surfaces.
|
|
|
[PDF]
|
|
|


|
|
¢¹ Songhee Han, Hyun Sik Yoo, Doo-Sik Ahn, Young S. Choi, and Sang Kyu Kim
|
|
|
|
"Vacuum ultraviolet mass-analyzed threshold ionization spectroscopy of
methylcyclohexane in the supersonic jet"
Chem. Phys. Lett., 518, 38 (2011)

Vacuum ultraviolet (VUV) mass-analyzed threshold ionization (MATI) spectrum of supersonically cooled methylcyclohexane has been obtained to give the precise adiabatic ionization energy of 9.6958 ± 0.0025 eV for the chair equatorial conformer. Vibrationally resolved MATI spectrum has been analyzed with the aid of density functional theory and Franck–Condon calculations. The MATI spectrum reflects the structural change upon ionization and its origin is discussed by inspecting the shapes of the valence orbitals involved in the ionization process. The spectroscopic implication of the structural interconversion above the certain energy level is discussed with theoretical calculations of molecular structures and energetics.
|
|
|
[PDF]
|
|
¢¹ Kuk Ki Kim, Daehyun Kim, Sang Kyu Kim, Seung Min Park, Jae Kyu Song
|
|
|
|
"Formation of ZnO nanoparticles by laser ablation in neat water"
Chem. Phys. Lett., 511, 116-120 (2011)
Zinc oxide (ZnO) nanoparticles were prepared in neat deionized water by laser ablation with various ablation times (10 – 40 min), fluences (50 – 130 mJ/pulse), and wavelengths (1064, 532, and 355 nm). The size and shape of the nanoparticles were affected only slightly by the ablation time and fluence at a wavelength of 1064 nm, which was explained by a dynamic formation mechanism with surface charge effects. The nanoparticles formed by ablation at 355 nm had a distinctive wire-shape with a small diameter, which was attributed to a continuous fragmentation and formation mechanism.
|
|
|
[PDF]
|
|
|

|
|
¢¹ SongHee Han, Hyun Sik You, Sang Kyu Kim
|
|
|
|
"Comformer-specific Ionization Spectroscopy of Bromocyclohexane:
Equatorial versus Axial conformers"
J. Phys. Chem. A, 2010, 114, 10005-10010
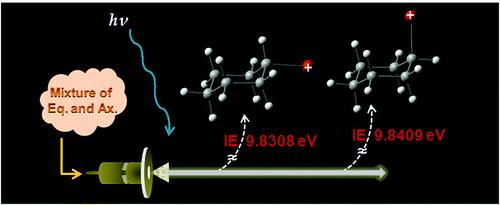
Ionization of equatorial and axial conformational isomers of the chair-bromocyclohexane is investigated with use of the vacuum ultraviolet mass-analyzed threshold ionization (MATI) spectroscopic technique. Two distinct ionization energies of 9.8308 ± 0.0025 and 9.8409 ± 0.0025 eV are determined for equatorial or axial conformers, respectively. From the conformer-selective vibrational analysis, it is found that the equatorial conformer undergoes a drastic structural change upon ionization especially along the C-Br distortion mode, whereas the axial conformer shows the modest change along the ring-puckering mode with ionization, corresponding to the reaction coordinate for the conformational interconversion. Density functional theory (DFT) calculations with and without considering the spin-orbit coupling provide the appropriate mode assignments for the vibrational bands active in the ionization spectra. Natural bond orbital (NBO) analysis is carried out to give insights into the contribution of the anomeric effect to the structure-energy relationship in each conformational isomer.
|
|
|
[PDF]
|
|
|
¢¹ Ki Young Yeon, Dahyi Jeong, Sang Kyu Kim
|
|
|
|
"Intrinsic lifetimes of the Soret bands of the free base tetraphenylporphine (H2TPP) and
Cu(II)TPP in the condensed phase"
Chem. Commun., 46, 5572-5574 (2010)

Soret band lifetimes of the free-base tetraphenylporphine (H2TPP) and Cu(II) tetraphenylporphine (CuIITPP) at 408 nm have been directly measured with femtosecond (fs) resolution using the fluorescence-upconversion technique for the first time, giving ¥ó = 68 ± 15 and 63 ± 15 fs, respectively, in benzene solvent.
|
|
|
[PDF]
|
|
|
¢¹ Songhee Han, N. Jiten Singh, Tae Yeon Kang, Kyo-Won Choi, Sunyoung Choi,
Sun Jong Baek, Kwang S. Kim, Sang Kyu Kim
|
|
|
|
"Aromatic ¥ð-¥ð interaction mediated by a metal atom: structure and ionization of the
bis(¥ç6-benzene)chromium benzene cluster"
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 12, 7648-7653 (2010)
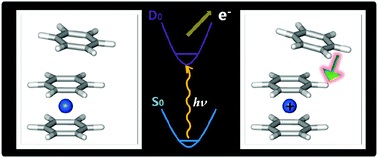
Aromatic ¥ð–¥ð interaction in the presence of a metal atom has been investigated experimentally and theoretically with the model system of bis(¥ç6-benzene)chromium–benzene cluster (Cr(Bz)2–Bz) in which a free solvating benzene is non-covalently attached to the benzene moiety of Cr(Bz)2. One-photon mass-analyzed threshold ionization (MATI) spectroscopy and first principles calculations are employed to identify the structure of Cr(Bz)2–Bz which adopts the parallel-displaced configuration. The decrease in ionization potential for Cr(Bz)2–Bz compared with Cr(Bz)2, resulting from the increase of the cation–¥ð stabilization energy upon ionization, is consistent with the parallel-displaced structure of the cluster. Theoretical calculations give the detailed cluster structures with associated energetics, thus revealing the nature of ¥ð–¥ð–metal or ¥ð–¥ð–cation interactions at the molecular level.
|
|
|
[PDF]
|
|
|
|
¢¹ Jeong Sik Lim, Sang Kyu Kim
|
|
|
|
"Experimental probing of conical intersection dynamics in the photodissociation of thioanisole"
Nature Chemistry, 2, 627-632 (2010)
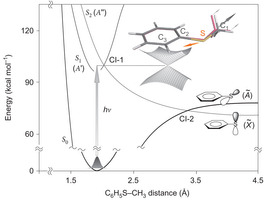 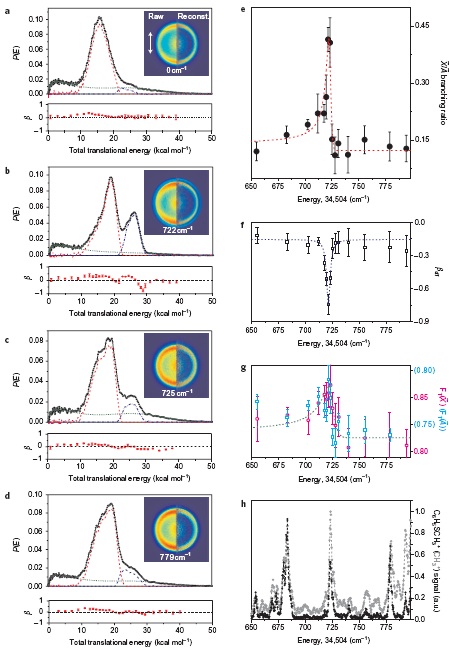
Direct experimental probing of conical intersections is rare but here, in studies of the photodissociation of thioanisole, a striking dependence of the non-adiabatic transition probability on photoexcitation energy has been observed, revealing the nuclear configuration of the conical intersection and its dynamic role in such transitions.
|
|
|
[PDF]
|
|
|
¢¹ Doo-Sik Ahn, So-Yeon Kim, Goo-Il Lim, Sungyul Lee, Young S. Choi, Sang Kyu Kim
|
|
|
|
"Mode-Dependent Fano Resonances Observed in the Predissociation of Diazirine in the S1 State"
Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 49, 7, 1244-1247 (2010) (selected as a VIP)
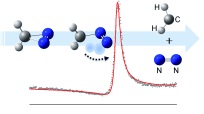
Lights, spectrometer, action: Crucial information about the detailed shape of the potential-energy surface in the vicinity of the transition state is obtained from the Fano resonances in the photodissociation cross-section of diazirine in the S1 state. The excitation along the asymmetric C-N stretching mode accelerates the ring-opening reaction, suggesting that two C-N bonds of the excited diazirine break in a stepwise manner (see scheme).
|
|
|
[PDF]
|
|
|
¢¹ Songhee Han, Tae Yeon Kang, Sang Kyu Kim
|
|
|
|
"Rotationally resolved spectroscopy of the 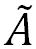 2A1 ¡ç 2A1 ¡ç 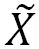 2B1 transition of H2S+ above the barrier to linearity 2B1 transition of H2S+ above the barrier to linearity
using the mass-analyzed threshold ionization photofragment excitation technique"
J. Chem. Phys., 132, 124304 (2010)
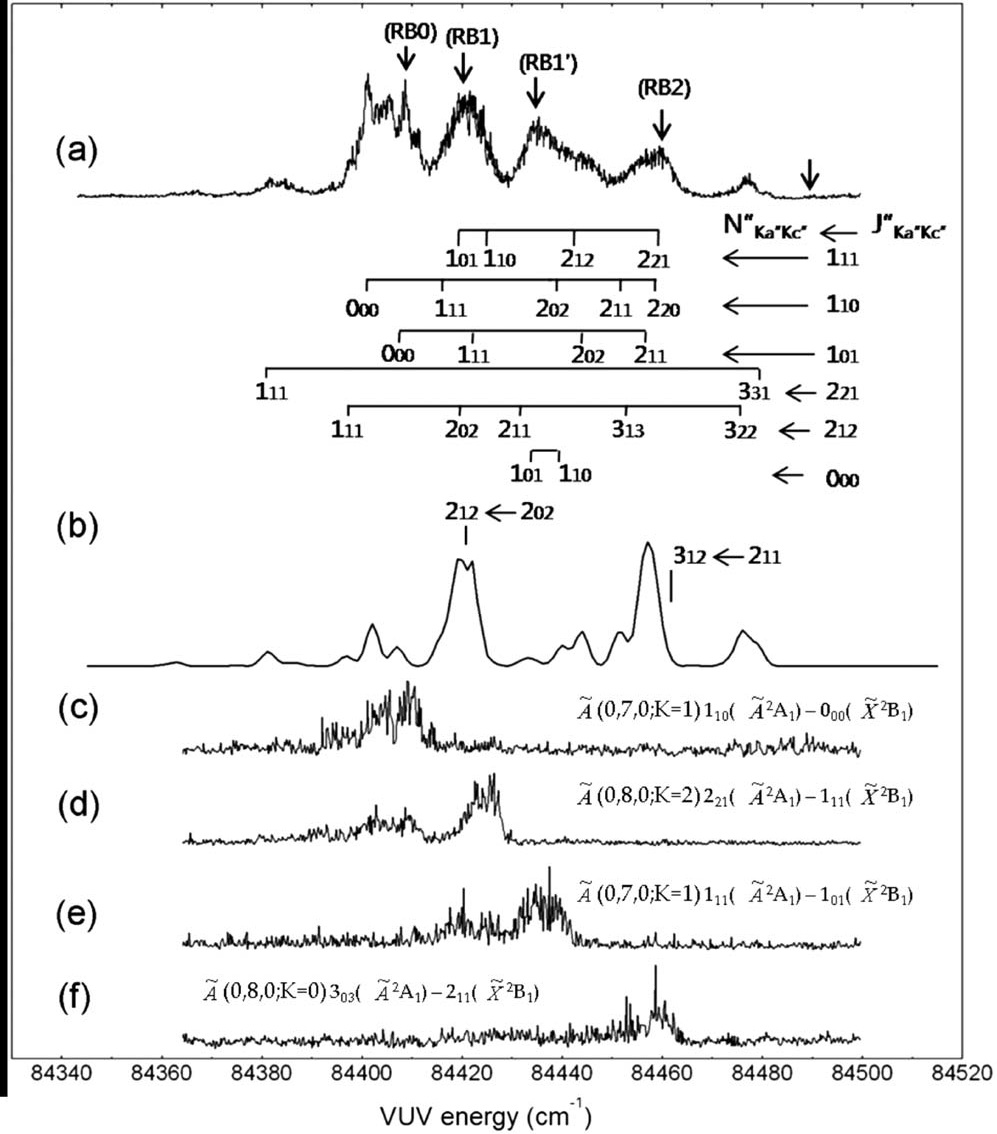 
The  2A1 ¡ç 2A1 ¡ç  2B1 transitions of H2S+ above the barrier to linearity have been investigated with the energy resolution high enough to identify individual rotational transition lines for the first time. The rotational cooling of the cation is achieved either by the direct ionization or mass-analyzed threshold ionization (MATI) technique employed in the vacuum-ultraviolet laser excitation of the jet-cooled H2S. Subsequent photoexcitation leads to the H2S+ ¡æ H2 + S+ dissociation and the S+ product yield taken as a function of the excitation energy gives the photofragment excitation (PHOFEX) spectra. The combined use of MATI and PHOFEX techniques greatly simplifies the spectrum allowing the accurate identification of the rotationally resolved bands which is otherwise a formidable task due to the intrinsic complexity of the 2B1 transitions of H2S+ above the barrier to linearity have been investigated with the energy resolution high enough to identify individual rotational transition lines for the first time. The rotational cooling of the cation is achieved either by the direct ionization or mass-analyzed threshold ionization (MATI) technique employed in the vacuum-ultraviolet laser excitation of the jet-cooled H2S. Subsequent photoexcitation leads to the H2S+ ¡æ H2 + S+ dissociation and the S+ product yield taken as a function of the excitation energy gives the photofragment excitation (PHOFEX) spectra. The combined use of MATI and PHOFEX techniques greatly simplifies the spectrum allowing the accurate identification of the rotationally resolved bands which is otherwise a formidable task due to the intrinsic complexity of the  2A1 ¡ç 2A1 ¡ç  2B1 transition. Highly excited states of 2B1 transition. Highly excited states of  (0,7,0), (0,7,0),  (0,8,0), and (0,8,0), and  (0,9,0) vibronic levels with different K quantum numbers which are located above the barrier to linearity are thoroughly investigated. The bent-to-quasilinear transition of H2S+ above the barrier to linearity shows the characteristics of the Renner–Teller effect, showing the large A rotational constant and strong intensity borrowing of the highly vibrationally excited ground levels such as (0,9,0) vibronic levels with different K quantum numbers which are located above the barrier to linearity are thoroughly investigated. The bent-to-quasilinear transition of H2S+ above the barrier to linearity shows the characteristics of the Renner–Teller effect, showing the large A rotational constant and strong intensity borrowing of the highly vibrationally excited ground levels such as  (0,23,0) or (0,23,0) or  (0,24,0) in the dipole-allowed excitation. Spectroscopic parameters of term values, rotational, and spin-orbit coupling constants are precisely determined in this work, providing the most quantitative spectroscopic structure of the H2S+ to date. Quantum-state dependent photodissociation dynamics are also discussed from spectral features of PHOFEX. (0,24,0) in the dipole-allowed excitation. Spectroscopic parameters of term values, rotational, and spin-orbit coupling constants are precisely determined in this work, providing the most quantitative spectroscopic structure of the H2S+ to date. Quantum-state dependent photodissociation dynamics are also discussed from spectral features of PHOFEX.
|
|
|
[PDF]
|
|
|
 Oleg Kostko,Sang Kyu Kim, Stephen R. Leone, Musahid Ahmed, "Mass-Analyzed Threshold Ionization (MATI) Spectroscopy of Atoms and Molecules Using
VUV Synchrotron Radiation", J. Phys. Chem. A, 113, 14206-14211 (2009).[PDF] Oleg Kostko,Sang Kyu Kim, Stephen R. Leone, Musahid Ahmed, "Mass-Analyzed Threshold Ionization (MATI) Spectroscopy of Atoms and Molecules Using
VUV Synchrotron Radiation", J. Phys. Chem. A, 113, 14206-14211 (2009).[PDF]
 Jeong Sik Lim, Heechol Choi, Ivan S. Lim, Seong Byung Park, Yoon Sup Lee,
Sang Kyu Kim, "Photodissociation Dynamics of Thiophenol-d1: The Nature of Excited Electronic States along the S-D Bond Dissociation Corrdinate", J.
Phys. Chem. A, 113, 10410-10416 (2009).[PDF] Jeong Sik Lim, Heechol Choi, Ivan S. Lim, Seong Byung Park, Yoon Sup Lee,
Sang Kyu Kim, "Photodissociation Dynamics of Thiophenol-d1: The Nature of Excited Electronic States along the S-D Bond Dissociation Corrdinate", J.
Phys. Chem. A, 113, 10410-10416 (2009).[PDF]
|
|
 Kyoung-Seok Lee,
Ki Young Yeon, Kyung-Hoon Jung,
Sang Kyu Kim, "Direct observation of the primary and secondary C-Br bond cleavages from the 1,2-dibromopropane photodissociation at 234 and 265 nm using the velocity map ion imaging technique", J.
Phys. Chem. A, vol.112, 9312-9317 (2008).[PDF] Kyoung-Seok Lee,
Ki Young Yeon, Kyung-Hoon Jung,
Sang Kyu Kim, "Direct observation of the primary and secondary C-Br bond cleavages from the 1,2-dibromopropane photodissociation at 234 and 265 nm using the velocity map ion imaging technique", J.
Phys. Chem. A, vol.112, 9312-9317 (2008).[PDF]
 Kyo-Won Choi, Sunyoung
Choi, Doo-Sik Ahn, Songhee Han, Tae Yeon Kang, Sun Jong Baek, Sang Kyu Kim, "Clustering dynamics of the metal-benzene sandwich
complex: the role of microscopic structure of the solute in the bis(¥ç6-benzene)chromium·Arn clusters (n=
1-15)", J.
Phys. Chem. A, 122, 7125-7127 (2008).[PDF] Kyo-Won Choi, Sunyoung
Choi, Doo-Sik Ahn, Songhee Han, Tae Yeon Kang, Sun Jong Baek, Sang Kyu Kim, "Clustering dynamics of the metal-benzene sandwich
complex: the role of microscopic structure of the solute in the bis(¥ç6-benzene)chromium·Arn clusters (n=
1-15)", J.
Phys. Chem. A, 122, 7125-7127 (2008).[PDF]
 Doo-Sik Ahn,
Kyo-Won Choi, Sun Jong Baek, Young S. Choi, Sungyul Lee, Heechol Choi, Kyoung
Koo Baeck, Sang Kyu Kim, "Structure of Pyridazine in the S1 state:
Experiment and Theory", ChemPhysChem, 9, 1610-1616 (2008)[PDF] Doo-Sik Ahn,
Kyo-Won Choi, Sun Jong Baek, Young S. Choi, Sungyul Lee, Heechol Choi, Kyoung
Koo Baeck, Sang Kyu Kim, "Structure of Pyridazine in the S1 state:
Experiment and Theory", ChemPhysChem, 9, 1610-1616 (2008)[PDF]
 Sunyoung
Choi, Kyo-Won Choi, Songhee Han, Doo-Sik Ahn, Tae Yeon Kang, Sun Jong Baek, Sang
Kyu Kim, "Conformationally specific vacuum-ultraviolet mass-analyzed
threshold ionization spectroscopy of alkanethiols: structure and ionization of
conformational isomers of ethanethiol, isopropanethiol, 1-propanethiol,
tert-butanethiol, and 1-butanethiol", J.
Phys. Chem. A, 122, 7191-7199 (2008).[PDF] Sunyoung
Choi, Kyo-Won Choi, Songhee Han, Doo-Sik Ahn, Tae Yeon Kang, Sun Jong Baek, Sang
Kyu Kim, "Conformationally specific vacuum-ultraviolet mass-analyzed
threshold ionization spectroscopy of alkanethiols: structure and ionization of
conformational isomers of ethanethiol, isopropanethiol, 1-propanethiol,
tert-butanethiol, and 1-butanethiol", J.
Phys. Chem. A, 122, 7191-7199 (2008).[PDF]
 Doo-Sik Ahn, Jeongmook Lee,
Jeong-Mo Choi, Kyoung-Seok Lee, Sun Jong Baek, Kunhye Lee, Kyoung-Koo Baeck,
Sang Kyu Kim, "State-selective predissociation dynamics of methylamines: the
vibronic and H/D effects on the conical intersection dynamics", J. Chem.
Phys., 128, 224305 (2008).[PDF] Doo-Sik Ahn, Jeongmook Lee,
Jeong-Mo Choi, Kyoung-Seok Lee, Sun Jong Baek, Kunhye Lee, Kyoung-Koo Baeck,
Sang Kyu Kim, "State-selective predissociation dynamics of methylamines: the
vibronic and H/D effects on the conical intersection dynamics", J. Chem.
Phys., 128, 224305 (2008).[PDF]
 Sunyoung
Choi, Tae Yeon Kang, Kyo-Won Choi, Songhee Han, Doo-Sik Ahn, Sun Jong Baek, and
Sang Kyu Kim, "Ionization spectroscopy of conformational isomers of
propanal: the origin of the conformational preference", J. Phys. Chem. A., 112, 5060–5063 (2008).[PDF] Sunyoung
Choi, Tae Yeon Kang, Kyo-Won Choi, Songhee Han, Doo-Sik Ahn, Sun Jong Baek, and
Sang Kyu Kim, "Ionization spectroscopy of conformational isomers of
propanal: the origin of the conformational preference", J. Phys. Chem. A., 112, 5060–5063 (2008).[PDF]
 Songhee Han, Tae Yeon
Kang, Sunyoung
Choi, Kyo-Won Choi,
Sun Jong Baek, Sungyul Lee
and
Sang Kyu Kim, ¡°One-photon ionization spectroscopy of jet-cooled
oxazole and thiazole: the role of oxygen and sulfur in the ¥ð-conjugation of
heterocyclic compounds¡± Phys.
Chem. Chem. Phys., 10, 3883 – 3887 (2008).[PDF] Songhee Han, Tae Yeon
Kang, Sunyoung
Choi, Kyo-Won Choi,
Sun Jong Baek, Sungyul Lee
and
Sang Kyu Kim, ¡°One-photon ionization spectroscopy of jet-cooled
oxazole and thiazole: the role of oxygen and sulfur in the ¥ð-conjugation of
heterocyclic compounds¡± Phys.
Chem. Chem. Phys., 10, 3883 – 3887 (2008).[PDF]
 Hoon Han,
Seong Byeong Park, Sang Kyu Kim, and Sukbok Chang, ¡°Copper-Nitrenoid Formation and Transfer in Catalytic Olefin Aziridination
Utilizing Chelating 2-Pyridylsulfonyl Moieties¡±, J. Org. Chem., 73, 2862
– 2870 (2008).[PDF] Hoon Han,
Seong Byeong Park, Sang Kyu Kim, and Sukbok Chang, ¡°Copper-Nitrenoid Formation and Transfer in Catalytic Olefin Aziridination
Utilizing Chelating 2-Pyridylsulfonyl Moieties¡±, J. Org. Chem., 73, 2862
– 2870 (2008).[PDF]
 Jeong Sik Lim, Yoon Sup Lee, and Sang Kyu Kim, "Control of the Intramolecular orbital alignment observed in the photodissociation of thiophenol: the conformational manipulation via the chemical substitution", Angew.
Chem. int. ed., 47, 10, 1853-1856 (2008) (selected as a VIP). [PDF] Jeong Sik Lim, Yoon Sup Lee, and Sang Kyu Kim, "Control of the Intramolecular orbital alignment observed in the photodissociation of thiophenol: the conformational manipulation via the chemical substitution", Angew.
Chem. int. ed., 47, 10, 1853-1856 (2008) (selected as a VIP). [PDF]
|
|
 Ho-Sung Kim, Doo-Sik Ahn, Sang-Yoon Chung, Sang Kyu Kim, SungyulLee, ¡°Tautomerization of adenine facilitated
by water: Computational study of microsolvation¡±, J. Phys. Chem. A, 111 (32),
8007, (2007). [PDF] Ho-Sung Kim, Doo-Sik Ahn, Sang-Yoon Chung, Sang Kyu Kim, SungyulLee, ¡°Tautomerization of adenine facilitated
by water: Computational study of microsolvation¡±, J. Phys. Chem. A, 111 (32),
8007, (2007). [PDF]
 Kyo-Won Choi, Doo-Sik Ahn, Joo-Hee Lee, and Sang Kyu Kim, ¡°A conformationally specific alpha- and beta-alanine decarboxylation pathway¡±, Chem. Commun. (9) 1041, (2007). [PDF] Kyo-Won Choi, Doo-Sik Ahn, Joo-Hee Lee, and Sang Kyu Kim, ¡°A conformationally specific alpha- and beta-alanine decarboxylation pathway¡±, Chem. Commun. (9) 1041, (2007). [PDF]
 Ivan S. Lim, Jung Sik Lim, Yoon Sup Lee, and Sang Kyu Kim, ¡°Experimental and theoretical study of photodissociation reaction of thiophenol at 243 nm: observation of the intramolecular orbital alignment¡±, J. Chem. Phys., 126, 034306, (2007). [PDF] Ivan S. Lim, Jung Sik Lim, Yoon Sup Lee, and Sang Kyu Kim, ¡°Experimental and theoretical study of photodissociation reaction of thiophenol at 243 nm: observation of the intramolecular orbital alignment¡±, J. Chem. Phys., 126, 034306, (2007). [PDF]
 Kyo-Won Choi, Sunyoung Choi, Sun Jong Baek and Sang Kyu Kim, ¡°Pulsed-field ionization spectroscopy of high Rydberg states (n = 50-200) of Bis(¥ç6-benzene)chromium¡±, J. Chem. Phys., 126, 034308, (2007). [PDF] Kyo-Won Choi, Sunyoung Choi, Sun Jong Baek and Sang Kyu Kim, ¡°Pulsed-field ionization spectroscopy of high Rydberg states (n = 50-200) of Bis(¥ç6-benzene)chromium¡±, J. Chem. Phys., 126, 034308, (2007). [PDF]
|
|
 Sunyoung Choi, Kyo-Won Choi, Sang Kyu Kim, Sangyoon Chung, and Sungyul Lee, ¡°Vibrational Structures of Dimethyl sulfide and Ethylene sulfide cations studied by Vacuum-UV mass-analyzed threshold ionization (MATI) spectroscopy¡± J. Phys. Chem. A, 110, 13183, (2006). [PDF] Sunyoung Choi, Kyo-Won Choi, Sang Kyu Kim, Sangyoon Chung, and Sungyul Lee, ¡°Vibrational Structures of Dimethyl sulfide and Ethylene sulfide cations studied by Vacuum-UV mass-analyzed threshold ionization (MATI) spectroscopy¡± J. Phys. Chem. A, 110, 13183, (2006). [PDF]
 Ji Min Lee, Doo-Sik Ahn, Doo Young Jung, Junseung Lee, Youngkyu Do, Sang Kyu Kim, and Sukbok Chang, "Hydrogen-Bond-Directed Highly Stereoselective Synthesis of Z-Enamides via Pd-Catalyzed Oxidative Amidation of Conjugated Olefins", J. Am. Chem. Soc., 128, 12954, (2006). [PDF] Ji Min Lee, Doo-Sik Ahn, Doo Young Jung, Junseung Lee, Youngkyu Do, Sang Kyu Kim, and Sukbok Chang, "Hydrogen-Bond-Directed Highly Stereoselective Synthesis of Z-Enamides via Pd-Catalyzed Oxidative Amidation of Conjugated Olefins", J. Am. Chem. Soc., 128, 12954, (2006). [PDF]
 Jeong Sik Lim, Ivan S. Lim, Kyoung-Seok Lee, Doo-Sik Ahn, Yoon Sup Lee, and Sang Kyu Kim, "Intramolecular orbital alignment observed in the photodissociation of thiophenol-d1", Angew. Chem. int. ed., 45, 6290, (2006) [PDF] Jeong Sik Lim, Ivan S. Lim, Kyoung-Seok Lee, Doo-Sik Ahn, Yoon Sup Lee, and Sang Kyu Kim, "Intramolecular orbital alignment observed in the photodissociation of thiophenol-d1", Angew. Chem. int. ed., 45, 6290, (2006) [PDF]
 Min Hee Park, Kyo-Won Choi, Sunyoung Choi, and Sang Kyu Kim, "Vibrational structures of methylamine isotopomers in the predissociative à states: CH3NHD, CD3NH2, CD3NHD, and CD3ND2", J. Chem. Phys., 125, 084311, (2006) [PDF] Min Hee Park, Kyo-Won Choi, Sunyoung Choi, and Sang Kyu Kim, "Vibrational structures of methylamine isotopomers in the predissociative à states: CH3NHD, CD3NH2, CD3NHD, and CD3ND2", J. Chem. Phys., 125, 084311, (2006) [PDF]
 Kyo-Won Choi, Doo-Sik Ahn, Joo-Hee Lee, Sang Kyu Kim, ¡°Vibrational Spectroscopy of the Pyridazine Cation in the Ground State¡±, J. Phys. Chem. A., 110 (8), 2634, (2006). [PDF] Kyo-Won Choi, Doo-Sik Ahn, Joo-Hee Lee, Sang Kyu Kim, ¡°Vibrational Spectroscopy of the Pyridazine Cation in the Ground State¡±, J. Phys. Chem. A., 110 (8), 2634, (2006). [PDF]
 Kyoung-Seok Lee, Jung-Sik Lim, Doo Sik Ahn, Kyo-Won Choi, Sang Kyu Kim, Young S. Choi, ¡°Nonadiabatic Dynamics in the Photodissociation of ICH2CN at 266 and 304 nm Using a Velocity Map Ion Imaging Technique¡±, J. Chem. Phys., 124, 124307,
(2006). [PDF] Kyoung-Seok Lee, Jung-Sik Lim, Doo Sik Ahn, Kyo-Won Choi, Sang Kyu Kim, Young S. Choi, ¡°Nonadiabatic Dynamics in the Photodissociation of ICH2CN at 266 and 304 nm Using a Velocity Map Ion Imaging Technique¡±, J. Chem. Phys., 124, 124307,
(2006). [PDF]
 Kyo-Won Choi, Joo-Hee Lee, Sang Kyu Kim, ¡°Vacuum-Ultraviolet Ionization Spectroscopy of the Jet-Cooled RNA-Base Uracil¡±, Chem. Commun., 1, 78, (2006). [PDF] Kyo-Won Choi, Joo-Hee Lee, Sang Kyu Kim, ¡°Vacuum-Ultraviolet Ionization Spectroscopy of the Jet-Cooled RNA-Base Uracil¡±, Chem. Commun., 1, 78, (2006). [PDF]
|
|


|
|
 Kyo-Won Choi, Joo-Hee Lee, Sang Kyu Kim, "Ionization Spectroscopy of a DNA Base: Vacuum-Ultraviolet Mass-Analyzed Threshold Ionization Spectroscopy of Jet-Cooled Thymine", J. Am. Chem. Soc.(Communication), 127, 15674, (2005). [PDF] Kyo-Won Choi, Joo-Hee Lee, Sang Kyu Kim, "Ionization Spectroscopy of a DNA Base: Vacuum-Ultraviolet Mass-Analyzed Threshold Ionization Spectroscopy of Jet-Cooled Thymine", J. Am. Chem. Soc.(Communication), 127, 15674, (2005). [PDF]
 In-Sun Jeon, Doo-Sik Ahn, Sung-Woo Park, Sungyul Lee, and S. K. Kim, "Structures and isomerization of serine in aqueous solution: Computational study", Chem. Phys. Lett., 403, 72-76 (2005). [PDF] In-Sun Jeon, Doo-Sik Ahn, Sung-Woo Park, Sungyul Lee, and S. K. Kim, "Structures and isomerization of serine in aqueous solution: Computational study", Chem. Phys. Lett., 403, 72-76 (2005). [PDF]
 Doo-Sik Ahn, Ae-Ri Kang, Sungyul Lee, Bongsoo Kim, Daniel Neuhauser, and S. K. Kim, "On the stability of glycine-water clusters with excess electron: Implications for photoelectron spectroscopy", J. Chem. Phys., 122, 84310 (2005). [PDF] Doo-Sik Ahn, Ae-Ri Kang, Sungyul Lee, Bongsoo Kim, Daniel Neuhauser, and S. K. Kim, "On the stability of glycine-water clusters with excess electron: Implications for photoelectron spectroscopy", J. Chem. Phys., 122, 84310 (2005). [PDF]
 Kyo-Won Choi, Doo-Sik Ahn, Sungyul Lee, and S. K. Kim, "One-Photon Mass-Analyzed Threshold Ioniization Spectroscopy of Bis(¥ç6-benzene)chromium and Its benzene and Ar Clusters", J. Phys. Chem. A, 108, 11292-11295 (2004). [PDF] Kyo-Won Choi, Doo-Sik Ahn, Sungyul Lee, and S. K. Kim, "One-Photon Mass-Analyzed Threshold Ioniization Spectroscopy of Bis(¥ç6-benzene)chromium and Its benzene and Ar Clusters", J. Phys. Chem. A, 108, 11292-11295 (2004). [PDF]
 K.-W. Choi, D.-S. Ahn, S. Lee, H. Choi, K.-K. Baeck, S.-U. Heo, S. J. Baek, Y. S. Choi, and S. K. Kim, ¡°Structural Distortion of Pyridazine in the 1(n,¥ð*) Excited State: Evidence for Local Excitation¡±, Chem. Phys. Chem., 5, 737-739 (2004). [PDF] K.-W. Choi, D.-S. Ahn, S. Lee, H. Choi, K.-K. Baeck, S.-U. Heo, S. J. Baek, Y. S. Choi, and S. K. Kim, ¡°Structural Distortion of Pyridazine in the 1(n,¥ð*) Excited State: Evidence for Local Excitation¡±, Chem. Phys. Chem., 5, 737-739 (2004). [PDF]
 S. Y. Chae, M. K. Park, S. K. Lee, T. Y. Kim, S. K. Kim, and W. I. Lee, ¡°Preparation of size-controlled TiO2 nanoparticles and derivation of optically transparent photocatalytic films¡±, Chem. Mater., 15, 3326-3331 (2003). [PDF] S. Y. Chae, M. K. Park, S. K. Lee, T. Y. Kim, S. K. Kim, and W. I. Lee, ¡°Preparation of size-controlled TiO2 nanoparticles and derivation of optically transparent photocatalytic films¡±, Chem. Mater., 15, 3326-3331 (2003). [PDF]
 Y. Masumoto, S. K. Kim, T. Suzuki, ¡°Femtosecond photoelectron imaging study of pyridazine: S1 lifetime and (3s,3p) Rydberg state energetics¡±, J. Chem. Phys., 119 (1), 300-303 (2003). [PDF] Y. Masumoto, S. K. Kim, T. Suzuki, ¡°Femtosecond photoelectron imaging study of pyridazine: S1 lifetime and (3s,3p) Rydberg state energetics¡±, J. Chem. Phys., 119 (1), 300-303 (2003). [PDF]
 S. J. Baek, K.-W. Choi, Y. S. Choi, and S. K. Kim, ¡°Spectroscopy and dynamics of methylamine II: rotational and vibrational structures of CH3NH2 and CH3ND2 in cationic D0 states¡± J. Chem. Phys., 118 (24), 11040-11047 (2003). [PDF] S. J. Baek, K.-W. Choi, Y. S. Choi, and S. K. Kim, ¡°Spectroscopy and dynamics of methylamine II: rotational and vibrational structures of CH3NH2 and CH3ND2 in cationic D0 states¡± J. Chem. Phys., 118 (24), 11040-11047 (2003). [PDF]
 S. J. Baek, K.-W. Choi, Y. S. Choi, and S. K. Kim, ¡°Spectroscopy and dynamics of methylamine I: rotational and vibrational structures of CH3NH2 and CH3ND2 in à states¡± J. Chem. Phys., 118 (24), 11026-11039 (2003). [PDF] S. J. Baek, K.-W. Choi, Y. S. Choi, and S. K. Kim, ¡°Spectroscopy and dynamics of methylamine I: rotational and vibrational structures of CH3NH2 and CH3ND2 in à states¡± J. Chem. Phys., 118 (24), 11026-11039 (2003). [PDF]
 S. J. Baek, K.-W. Choi, Y. S. Choi, and S. K. Kim, ¡°First excited and cationic ground states of jet-cooled 2-aminopyridines · Arn (n=1,2) clusters: energetics and structures¡±, J. Phys. Chem. A, 107 (24), 4826-4828 (2003). [PDF] S. J. Baek, K.-W. Choi, Y. S. Choi, and S. K. Kim, ¡°First excited and cationic ground states of jet-cooled 2-aminopyridines · Arn (n=1,2) clusters: energetics and structures¡±, J. Phys. Chem. A, 107 (24), 4826-4828 (2003). [PDF]
 S. J. Baek, K.-W. Choi, Y. S. Choi, and S. K. Kim, ¡°Vibrational structures of predissociating methylamines (CH3NH2 and CH3ND2) in à states: Free internal rotation of CH3 with respect to NH2¡±, J. Chem. Phys., 117 (22), 10057 (2002). [PDF] S. J. Baek, K.-W. Choi, Y. S. Choi, and S. K. Kim, ¡°Vibrational structures of predissociating methylamines (CH3NH2 and CH3ND2) in à states: Free internal rotation of CH3 with respect to NH2¡±, J. Chem. Phys., 117 (22), 10057 (2002). [PDF]
 S. J. Baek, K.-W. Choi, Y. S. Choi, and S. K. Kim, ¡°Resonant-enhanced two-photon ionization and mass-analyzed threshold ionization spectroscopy of jet-cooled 2-aminopyridines (2AP-NH2, -ND2, -NHD, and -NDH)¡±, J. Chem. Phys., 117(5), 2131-2140 (2002). [PDF] S. J. Baek, K.-W. Choi, Y. S. Choi, and S. K. Kim, ¡°Resonant-enhanced two-photon ionization and mass-analyzed threshold ionization spectroscopy of jet-cooled 2-aminopyridines (2AP-NH2, -ND2, -NHD, and -NDH)¡±, J. Chem. Phys., 117(5), 2131-2140 (2002). [PDF]
 S. J. Baek, D. Lee, K.-W. Choi, Y. S. Choi, and S. K. Kim, ¡°Torsional vibrational levels combined with higher frequency modes of the jet-cooled p-methoxybenzyl alcohol in the S1 excited state¡±, J. Mol. Structure, 611(1-3), 203-211 (2002). [PDF] S. J. Baek, D. Lee, K.-W. Choi, Y. S. Choi, and S. K. Kim, ¡°Torsional vibrational levels combined with higher frequency modes of the jet-cooled p-methoxybenzyl alcohol in the S1 excited state¡±, J. Mol. Structure, 611(1-3), 203-211 (2002). [PDF]
 T. S. Kim, K.-W. Choi, S. K. Kim, Y. S. Choi, S. W. Park, D. S. Ahn, S. Lee, and K. Yoshihara, ¡°Fluorescence excitation spectroscopy of octatetraene-Xe van der Waals clusters¡±, Bull. Korean Chem. Soc., 23(2), 195-200 (2002). [PDF] T. S. Kim, K.-W. Choi, S. K. Kim, Y. S. Choi, S. W. Park, D. S. Ahn, S. Lee, and K. Yoshihara, ¡°Fluorescence excitation spectroscopy of octatetraene-Xe van der Waals clusters¡±, Bull. Korean Chem. Soc., 23(2), 195-200 (2002). [PDF]
 D. Lee, S. J. Baek, K.-W. Choi, Y. S. Choi, and S. K. Kim, ¡°Resonantly-enhanced two-photon ionization and mass-analyzed threshold ionization (MATI) spectroscopy of 2-hydroxypyridine¡±, Bull. Korean Chem. Soc., 23(2), 277-280 (2002). [PDF] D. Lee, S. J. Baek, K.-W. Choi, Y. S. Choi, and S. K. Kim, ¡°Resonantly-enhanced two-photon ionization and mass-analyzed threshold ionization (MATI) spectroscopy of 2-hydroxypyridine¡±, Bull. Korean Chem. Soc., 23(2), 277-280 (2002). [PDF]
 S. T. Park, S. K. Kim, M. S. Kim, ¡°Observation of conformation-specific pathways in the photodissociation of 1-iodopropane ions¡±, Nature, 415, 306-308 (2002). [PDF] S. T. Park, S. K. Kim, M. S. Kim, ¡°Observation of conformation-specific pathways in the photodissociation of 1-iodopropane ions¡±, Nature, 415, 306-308 (2002). [PDF]
 W.-H. Park, S. H. Cho, H. Cho, S. K. Kim, and Y. S. Choi, ¡°Ultraviolet Photolysis of 1,6-Methano[10]annulene Generates the Singlet Methylene¡±, Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 22(9), 1030-1032 (2001). [PDF] W.-H. Park, S. H. Cho, H. Cho, S. K. Kim, and Y. S. Choi, ¡°Ultraviolet Photolysis of 1,6-Methano[10]annulene Generates the Singlet Methylene¡±, Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 22(9), 1030-1032 (2001). [PDF]
 S. K. Shin, S. K. Kim, H. L. Kim, and C. R. Park, ¡°Two photon dissociation of acetone, acetaldehyde, and acetic acid at 243 nm: translational energy release in the H atom channel¡±, J. Photochemistry and Photobiology A: Chemistry 143, 11-16 (2001). [PDF] S. K. Shin, S. K. Kim, H. L. Kim, and C. R. Park, ¡°Two photon dissociation of acetone, acetaldehyde, and acetic acid at 243 nm: translational energy release in the H atom channel¡±, J. Photochemistry and Photobiology A: Chemistry 143, 11-16 (2001). [PDF]
 H. T. Kwon, S. K. Shin, S. K. Kim, H. L. Kim, and C. R. Park, ¡°Photodissociation dynamics of acetic acid and trifluoroacetic acid at 193 nm¡±, J. Phys. Chem. A 105 (28), 6775-6779 (2001).[PDF] H. T. Kwon, S. K. Shin, S. K. Kim, H. L. Kim, and C. R. Park, ¡°Photodissociation dynamics of acetic acid and trifluoroacetic acid at 193 nm¡±, J. Phys. Chem. A 105 (28), 6775-6779 (2001).[PDF]
 S. T. Park, S. K. Kim, and M. S. Kim, ¡°Vacuum-ultraviolet mass-analysed threshold ionization spectra of iodobutane isomers: conformer-specific ionization and ion-core dissociation followed by ionization¡±, J. Chem. Phys. 115 (6), 2492-2498 (2001).
[PDF] S. T. Park, S. K. Kim, and M. S. Kim, ¡°Vacuum-ultraviolet mass-analysed threshold ionization spectra of iodobutane isomers: conformer-specific ionization and ion-core dissociation followed by ionization¡±, J. Chem. Phys. 115 (6), 2492-2498 (2001).
[PDF]
 S. T. Park, S. K. Kim, and M. S. Kim, ¡°One-photon mass-analysed threshold ionization spectroscopy of 1- and 2-iodopropanes in vacuum ultraviolet¡±, J. Chem. Phys. 114 (13), 5568-5576 (2001). [PDF] S. T. Park, S. K. Kim, and M. S. Kim, ¡°One-photon mass-analysed threshold ionization spectroscopy of 1- and 2-iodopropanes in vacuum ultraviolet¡±, J. Chem. Phys. 114 (13), 5568-5576 (2001). [PDF]
|
|


|
|
 S. H. Cho, W.-H. Park, S. K. Kim, and Y. S. Choi, "Unimolecular dissociation dynamics of vinyl chloride on the ground potential energy surface: the method of excitation and product state distributions of HCl and Cl fragments¡±,
J. Phys. Chem. A. 104(45), 10482-10488 (2000). [PDF] S. H. Cho, W.-H. Park, S. K. Kim, and Y. S. Choi, "Unimolecular dissociation dynamics of vinyl chloride on the ground potential energy surface: the method of excitation and product state distributions of HCl and Cl fragments¡±,
J. Phys. Chem. A. 104(45), 10482-10488 (2000). [PDF]
 M.-C. Yoon, S. J. Baek, H. Cho, Y. S. Choi, S. K. Kim, "Supersonic jet spectroscopic study of p-methoxybenzyl M.-C. Yoon, S. J. Baek, H. Cho, Y. S. Choi, S. K. Kim, "Supersonic jet spectroscopic study of p-methoxybenzyl
alcohol", J. Phys. Chem. A. 104(45), 10173-10178 (2000). [PDF]
 M.-C. Yoon, Y. S. Choi, S. K. Kim, "The OH product state distribution from the photodissociation of hexafloroacetylacetone", J. Phys. Chem. A, 104(19), 4352-4355 (2000). Chem. Phys. (Commu), 111, 456-459 (1999). M.-C. Yoon, Y. S. Choi, S. K. Kim, "The OH product state distribution from the photodissociation of hexafloroacetylacetone", J. Phys. Chem. A, 104(19), 4352-4355 (2000). Chem. Phys. (Commu), 111, 456-459 (1999).
[PDF]
 G.-I. Lim, S.-M. Lim, S. K. Kim,
and Young S. Choi, "Unexpectedly large O37ClO/O35ClO intensity ratios of the fluorescence from the low-energy vibrational levels of OClO (A2A2)", J. Chem. Phys. (Commu), 111,
456-459 (1999). [PDF] G.-I. Lim, S.-M. Lim, S. K. Kim,
and Young S. Choi, "Unexpectedly large O37ClO/O35ClO intensity ratios of the fluorescence from the low-energy vibrational levels of OClO (A2A2)", J. Chem. Phys. (Commu), 111,
456-459 (1999). [PDF]
 M.-C. Yoon, Y. S. Choi, S. K. Kim,
"Photodissociation Dynamics of acetylacetone: the OH product state
distribution", J. Chem. Phys. 110, 11850-11855 (1999). [PDF] M.-C. Yoon, Y. S. Choi, S. K. Kim,
"Photodissociation Dynamics of acetylacetone: the OH product state
distribution", J. Chem. Phys. 110, 11850-11855 (1999). [PDF]
 S.-M. Lim, G.-I. Lim, T.-S. Kim, S.
K. Kim, Y. S. Choi, "Fluorescence excitation spectrum of OClO
(A2A2)", J. Phys. Chem. A, 103 (13),
2097-2099 (1999).
[PDF] S.-M. Lim, G.-I. Lim, T.-S. Kim, S.
K. Kim, Y. S. Choi, "Fluorescence excitation spectrum of OClO
(A2A2)", J. Phys. Chem. A, 103 (13),
2097-2099 (1999).
[PDF]
 M.-C. Yoon, Y. S. Choi, S. K.
Kim, "Fluorescence excitation spectroscopic study of the jet-cooled acetyl
cyanide", J. Chem. Phys., 110, 7185-7191
(1999).
[PDF] M.-C. Yoon, Y. S. Choi, S. K.
Kim, "Fluorescence excitation spectroscopic study of the jet-cooled acetyl
cyanide", J. Chem. Phys., 110, 7185-7191
(1999).
[PDF]
 G.-I. Lim, M.-C. Yoon, S.-M. Lim, T.-S. Kim, S. K. Kim, Y. S. Choi, I. Kwak, "Fluorescence excitation spectroscopy of the jet-cooled dimethyldiazirine: the CH3 torsional mode assignment", Bull. Korean Chem. Soc., 20(3), 365-366 (1999). G.-I. Lim, M.-C. Yoon, S.-M. Lim, T.-S. Kim, S. K. Kim, Y. S. Choi, I. Kwak, "Fluorescence excitation spectroscopy of the jet-cooled dimethyldiazirine: the CH3 torsional mode assignment", Bull. Korean Chem. Soc., 20(3), 365-366 (1999).
 M.-C. Yoon, Y. S. Choi, S. K. Kim, "The OH production from the ¥ð-¥ð* transition of acetylacetone", Chem. Phys. Letters, 300, 207 (1999). [PDF] M.-C. Yoon, Y. S. Choi, S. K. Kim, "The OH production from the ¥ð-¥ð* transition of acetylacetone", Chem. Phys. Letters, 300, 207 (1999). [PDF]
 T.-S. Kim, S. K. Kim, Y. S. Choi, I. Kwak, "Laser-Induced Fluorescence Spectroscopy of the S1-S0 (1B2-1A1) Transition of Dimethyldiazirine", Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 19, 1042 (1998). T.-S. Kim, S. K. Kim, Y. S. Choi, I. Kwak, "Laser-Induced Fluorescence Spectroscopy of the S1-S0 (1B2-1A1) Transition of Dimethyldiazirine", Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 19, 1042 (1998).
 S.-M. Lim, T.-S. Kim, G.-I. Lim, S. K. Kim, Y. S. Choi, "Direct formation of CH2(b1B1) in the near-UV photodissociation of diazirine", Chem. Phys. Letters 288, 828 (1998).[PDF] S.-M. Lim, T.-S. Kim, G.-I. Lim, S. K. Kim, Y. S. Choi, "Direct formation of CH2(b1B1) in the near-UV photodissociation of diazirine", Chem. Phys. Letters 288, 828 (1998).[PDF]
 T.-S. Kim, S. K. Kim, Y. S. Choi, I. Kwak, "On
the second electronic state near the S1 state in
dimethyldiazirine",J. Chem. Phys. 107, 8719
(1997).
[PDF] T.-S. Kim, S. K. Kim, Y. S. Choi, I. Kwak, "On
the second electronic state near the S1 state in
dimethyldiazirine",J. Chem. Phys. 107, 8719
(1997).
[PDF]
 E. A. Wade, H. Clauberg, S. K. Kim, A. Mellinger, C. B. Moore, "Dynamics of Rotational Energy Release for Dissociation of Singlet Ketene and the Singlet/Triplet Branching Ratio", J. Phys. Chem. A 101, 732 (1997). [PDF] E. A. Wade, H. Clauberg, S. K. Kim, A. Mellinger, C. B. Moore, "Dynamics of Rotational Energy Release for Dissociation of Singlet Ketene and the Singlet/Triplet Branching Ratio", J. Phys. Chem. A 101, 732 (1997). [PDF]
 S. K. Kim, E. R. Lovejoy, C. B. Moore, "Dynamics
at Unimolecular Transition States", in Gas-Phase Chemical S. K. Kim, E. R. Lovejoy, C. B. Moore, "Dynamics
at Unimolecular Transition States", in Gas-Phase Chemical
Reaction Systems: Experiments and Models 100 Years after Max Bodenstein, ed. by J. Wolfrum, H.-R. Volpp, R. Rannacher, J. Warnatz, Springer Series in Chemical
Physics No.61 (Springer Berlin, Heidelberg, 1996) p.67.
 S. K. Kim, J. Guo, J. S. Baskin, A. H. Zewail,
"Femtosecond Chemically Activated Reactions: Concept of Nonstatistical Activation at High Thermal Energies", J. Phys. Chem. 100,
9202 (1996).
[PDF] S. K. Kim, J. Guo, J. S. Baskin, A. H. Zewail,
"Femtosecond Chemically Activated Reactions: Concept of Nonstatistical Activation at High Thermal Energies", J. Phys. Chem. 100,
9202 (1996).
[PDF]
 S. K. Kim, A. H. Zewail,
"Femtosecond elementary dynamics of transition states and asymmetric ¥á-cleavage in Norrish reaction", Chem. Phys. Letters 250, 279
(1996).
[PDF] S. K. Kim, A. H. Zewail,
"Femtosecond elementary dynamics of transition states and asymmetric ¥á-cleavage in Norrish reaction", Chem. Phys. Letters 250, 279
(1996).
[PDF]
|
|

|
|
 A. Douhal, S. K. Kim, A. H. Zewail, "Femtosecond molecular dynamics of tautomerization in model base pairs", Nature 378, 260 (1995). [PDF] A. Douhal, S. K. Kim, A. H. Zewail, "Femtosecond molecular dynamics of tautomerization in model base pairs", Nature 378, 260 (1995). [PDF]
 S. K. Kim, S. Pedersen, A. H. Zewail, "Direct Femtosecond Observation of the Transient Intermediate in the ¥á-Cleavage Reaction of (CH3)2CO to 2CH3 + CO: Resolving the Issue of Concertedness", J. Chem. Phys. 103, 477 (1995). [PDF] S. K. Kim, S. Pedersen, A. H. Zewail, "Direct Femtosecond Observation of the Transient Intermediate in the ¥á-Cleavage Reaction of (CH3)2CO to 2CH3 + CO: Resolving the Issue of Concertedness", J. Chem. Phys. 103, 477 (1995). [PDF]
 S. K. Kim, J. J. Breen, D. W. Willberg, L. W. Peng, A. Heikal, J. A. Syage, A. H. Zewail, "Solvation Ultrafast Dynamics of Reactions 8: Acid-Base Reactions in Finite-Sized Clusters of Naphthol in Ammonia, Water, and Piperidine", J. Phys. Chem.
99, 7421 (1995). [PDF] S. K. Kim, J. J. Breen, D. W. Willberg, L. W. Peng, A. Heikal, J. A. Syage, A. H. Zewail, "Solvation Ultrafast Dynamics of Reactions 8: Acid-Base Reactions in Finite-Sized Clusters of Naphthol in Ammonia, Water, and Piperidine", J. Phys. Chem.
99, 7421 (1995). [PDF]
 S. K. Kim, S. Pedersen, A. H. Zewail, "Femtochemistry of Organometallics: Dynamics of Metal-Metal and Metal-Ligand Bond Cleavage in M2(CO)10", Chem. Phys. Letters 233, 500 (1995). [PDF] S. K. Kim, S. Pedersen, A. H. Zewail, "Femtochemistry of Organometallics: Dynamics of Metal-Metal and Metal-Ligand Bond Cleavage in M2(CO)10", Chem. Phys. Letters 233, 500 (1995). [PDF]
 S. K. Kim, E. R. Lovejoy, C. B. Moore, "Transition-State Vibrational Level Thresholds for the Dissociation of Triplet Ketene", J. Chem. Phys. 102, 3202 (1995). [PDF] S. K. Kim, E. R. Lovejoy, C. B. Moore, "Transition-State Vibrational Level Thresholds for the Dissociation of Triplet Ketene", J. Chem. Phys. 102, 3202 (1995). [PDF]
 S. K. Kim, J.-K. Wang, A. H. Zewail, "Femtosecond pH jump: Dynamics of Acid-Base Reactions in Solvent Cages", S. K. Kim, J.-K. Wang, A. H. Zewail, "Femtosecond pH jump: Dynamics of Acid-Base Reactions in Solvent Cages",
Chem. Phys. Letters 228, 369 (1994). [PDF]
 E. R. Lovejoy, S. K. Kim, C. B. Moore, "Observation of Transition-State Vibrational Thresholds in the Rate of Dissociation of Ketene", Science 256, 1541 (1992). [PDF] E. R. Lovejoy, S. K. Kim, C. B. Moore, "Observation of Transition-State Vibrational Thresholds in the Rate of Dissociation of Ketene", Science 256, 1541 (1992). [PDF]
 E. R. Lovejoy, S. K. Kim, R. A. Alvarez, C. B. Moore, "Kinetics of Intramolecular Carbon Atom Exchange in Ketene", J. Chem. Phys. 95, 4081 (1991). [PDF] E. R. Lovejoy, S. K. Kim, R. A. Alvarez, C. B. Moore, "Kinetics of Intramolecular Carbon Atom Exchange in Ketene", J. Chem. Phys. 95, 4081 (1991). [PDF]
 S. K. Kim, Y. S. Choi, C. D. Pibel, Q.-K. Zheng, C. B. Moore, "Determination of the Singlet/Triplet Branching Ratio in the Photodissociation of Ketene", J. Chem. Phys. 94, 1954 (1991). [PDF] S. K. Kim, Y. S. Choi, C. D. Pibel, Q.-K. Zheng, C. B. Moore, "Determination of the Singlet/Triplet Branching Ratio in the Photodissociation of Ketene", J. Chem. Phys. 94, 1954 (1991). [PDF]
 C. B. Moore, Q.-K. Zheng, Y. S. Choi, W. H. Green, S. K. Kim, A. J. Mahoney, W. H. Miller, C. D. Pibel, W. F. Polik, P. Teal, "The High-Resolution Spectroscopy of Dissociating Molecules", Phil. Trans. R. Soc. Lond.
A 332, 297 (1990). C. B. Moore, Q.-K. Zheng, Y. S. Choi, W. H. Green, S. K. Kim, A. J. Mahoney, W. H. Miller, C. D. Pibel, W. F. Polik, P. Teal, "The High-Resolution Spectroscopy of Dissociating Molecules", Phil. Trans. R. Soc. Lond.
A 332, 297 (1990).
 S. K. Kim, M. S. Kim, S. W. Suh, "Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering (SERS) of Aromatic Amino Acids and their Glycyl Peptides", Journal of Raman Spectroscopy 18, 171 (1987). S. K. Kim, M. S. Kim, S. W. Suh, "Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering (SERS) of Aromatic Amino Acids and their Glycyl Peptides", Journal of Raman Spectroscopy 18, 171 (1987).
 S. K. Kim, T. H. Joo, S. W. Suh, M. S. Kim, "Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering (SERS) of Nucleic Acids: Adenine Series", Journal of Raman Spectroscopy 17, 381 (1986). S. K. Kim, T. H. Joo, S. W. Suh, M. S. Kim, "Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering (SERS) of Nucleic Acids: Adenine Series", Journal of Raman Spectroscopy 17, 381 (1986).
 K. W. Kim, S. K. Kim, M. S. Kim, S. W. Suh, "Raman Spectroscopic study of 5'-rGMP sol", Biopolymers 25, 753 (1986). K. W. Kim, S. K. Kim, M. S. Kim, S. W. Suh, "Raman Spectroscopic study of 5'-rGMP sol", Biopolymers 25, 753 (1986).
 S. B. Hong, S. K. Kim, M. S. Kim, S. W. Suh, "The Preliminary X-ray and Raman Study of GramicidinS:HCl", Archives of Biochemisty and Biophysics 243, 563 (1985). S. B. Hong, S. K. Kim, M. S. Kim, S. W. Suh, "The Preliminary X-ray and Raman Study of GramicidinS:HCl", Archives of Biochemisty and Biophysics 243, 563 (1985).
 S. K. Kim, M. S. Kim, S. W. Suh, "Kinetics of Hydrogen/Deuterium Exchange in 8-CH of 5-rAMP", Bulletin of Korean Chemical Society 6, 270 (1985). S. K. Kim, M. S. Kim, S. W. Suh, "Kinetics of Hydrogen/Deuterium Exchange in 8-CH of 5-rAMP", Bulletin of Korean Chemical Society 6, 270 (1985).

|
|
|

















































